Rosalia (festival) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In the
 In Greece and Rome, wreaths and garlands of flowers and greenery were worn by both men and women for festive occasions. Garlands of roses and violets, combined or singly, adorn erotic scenes, bridal processions, and drinking parties in Greek lyric poetry from the Archaic period onward. In
In Greece and Rome, wreaths and garlands of flowers and greenery were worn by both men and women for festive occasions. Garlands of roses and violets, combined or singly, adorn erotic scenes, bridal processions, and drinking parties in Greek lyric poetry from the Archaic period onward. In 
 Roses had funerary significance in Greece, but were particularly associated with death and entombment among the Romans. In Greece, roses appear on funerary
Roses had funerary significance in Greece, but were particularly associated with death and entombment among the Romans. In Greece, roses appear on funerary  Conversely, roses in a funerary context can allude to festive banqueting, since Roman families met at burial sites on several occasions throughout the year for libations and a shared meal that celebrated both the cherished memory of the beloved dead and the continuity of life through the family line. In Roman tomb painting, red roses often spill bountifully onto light ground. These ageless flowers created a perpetual Rosalia and are an expression of Roman beliefs in the soul's continued existence.
The bones or ashes of the deceased may be imagined as generating flowers, as in one Latin epitaph that reads:
Conversely, roses in a funerary context can allude to festive banqueting, since Roman families met at burial sites on several occasions throughout the year for libations and a shared meal that celebrated both the cherished memory of the beloved dead and the continuity of life through the family line. In Roman tomb painting, red roses often spill bountifully onto light ground. These ageless flowers created a perpetual Rosalia and are an expression of Roman beliefs in the soul's continued existence.
The bones or ashes of the deceased may be imagined as generating flowers, as in one Latin epitaph that reads:
 Although the rose had a long tradition in funerary art, the earliest record of a Roman rose festival named as such dates to the reign of
Although the rose had a long tradition in funerary art, the earliest record of a Roman rose festival named as such dates to the reign of  At
At  In Imperial-era Macedonia, several inscriptions mention the Rosalia as a commemorative festival funded by bequests to groups such as a ''vicianus'', a village or neighborhood association (from ''
In Imperial-era Macedonia, several inscriptions mention the Rosalia as a commemorative festival funded by bequests to groups such as a ''vicianus'', a village or neighborhood association (from ''

 In keeping with its theme of new growth and transformation, the Anthesteria was also the occasion for a
In keeping with its theme of new growth and transformation, the Anthesteria was also the occasion for a
 The
The
 The rites of Adonis ''( Adoneia)'' also came to be regarded as a Rosalia in the Imperial era. In one version of the myth, blood from Aphrodite's foot, pricked by a thorn, dyes the flowers produced from the body of Adonis when he is killed by the boar. In the ''Lament for Adonis'' attributed to Bion (2nd century BC), the tears of Aphrodite match the blood shed by Adonis drop by drop,
The rites of Adonis ''( Adoneia)'' also came to be regarded as a Rosalia in the Imperial era. In one version of the myth, blood from Aphrodite's foot, pricked by a thorn, dyes the flowers produced from the body of Adonis when he is killed by the boar. In the ''Lament for Adonis'' attributed to Bion (2nd century BC), the tears of Aphrodite match the blood shed by Adonis drop by drop,
 From the reign of
From the reign of  The exceptionally beautiful Attis grows up favored by the Mother of the Gods and by Agdistis, who is his constant companion. Under the influence of wine, Attis reveals that his accomplishments as a hunter are owing to divine favor—an explanation for why wine is religiously prohibited ''(
The exceptionally beautiful Attis grows up favored by the Mother of the Gods and by Agdistis, who is his constant companion. Under the influence of wine, Attis reveals that his accomplishments as a hunter are owing to divine favor—an explanation for why wine is religiously prohibited ''(
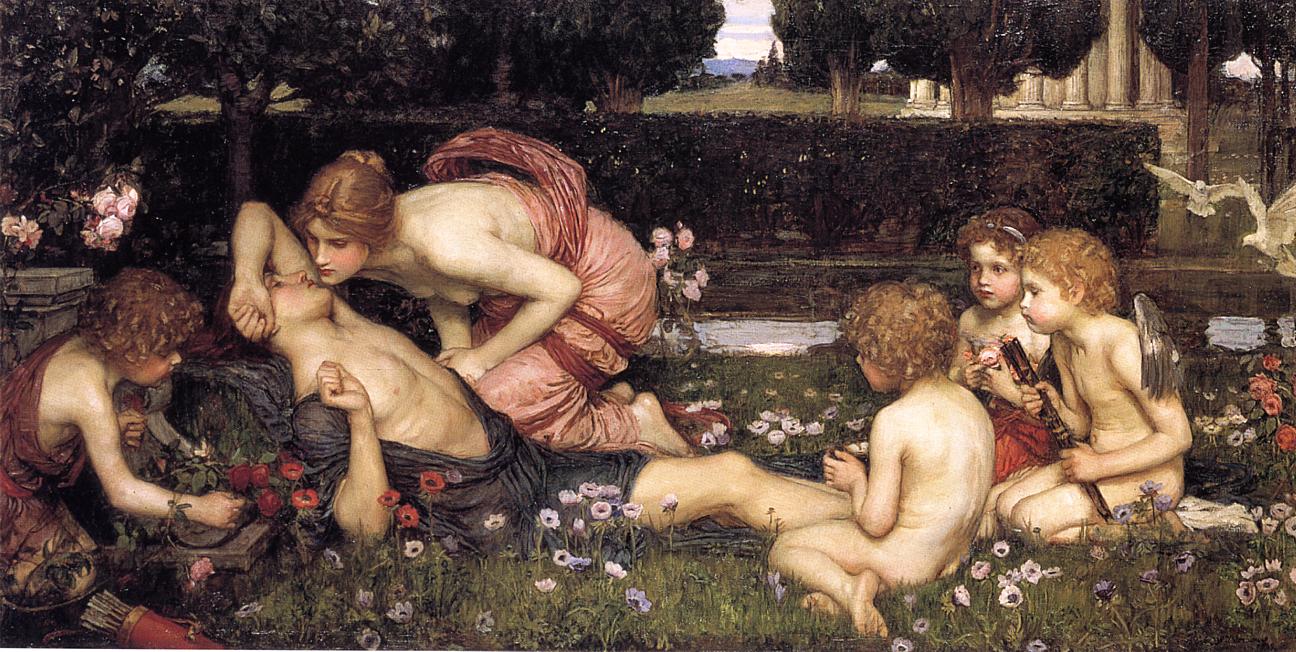
 In the later Empire, rose festivals became part of the iconography for the month of May. The date would vary locally to accommodate the blooming season. For month allegories in mosaics, May is often represented with floral wreaths, the fillets or ribbons worn for sacrifice, and wine
In the later Empire, rose festivals became part of the iconography for the month of May. The date would vary locally to accommodate the blooming season. For month allegories in mosaics, May is often represented with floral wreaths, the fillets or ribbons worn for sacrifice, and wine  Although the month opened with the revelry of Flora, in mid-May the Romans observed the three-day Lemuria for propitiating the wandering dead. The season of roses thus coincided with traditional Roman festivals pertaining to blooming and dying. The demand for flowers and perfumes for festal and funerary purposes made
Although the month opened with the revelry of Flora, in mid-May the Romans observed the three-day Lemuria for propitiating the wandering dead. The season of roses thus coincided with traditional Roman festivals pertaining to blooming and dying. The demand for flowers and perfumes for festal and funerary purposes made
 In the 6th century, a "Day of Roses" was held at Gaza, in the
In the 6th century, a "Day of Roses" was held at Gaza, in the  Miracle of the roses, Miracles involving roses are ascribed to some female saints, while roses are a distinguishing attribute of others ranging from Cecilia of Rome (d. 230 AD) to Thérèse of Lisieux (d. 1897). The floral iconography of Saint Cecilia includes a rose or floral wreath, a palm branch (symbol), palm branch, and a "tall sprig of almond leaves and flowers in her hand". Roses are among the most characteristic attributes of Mary, mother of Jesus, who became associated with the month of May, replacing goddesses such as Maia and Flora in the popular imagination. Mary is described in early Christian literature as a ''rosa pudoris'', "rose of modesty", and a rose among thorns. In the Middle Ages, roses, lilies and violets become the special flowers of Mary. In some Catholic cultures, offerings of flowers are still made to Mary, notably in Roman Catholicism in Mexico, Mexican devotional practices for Our Lady of Guadalupe. On the island of Pollap, in Micronesia, offerings of flowers before the cult statue of Mary are added to ceremonies of the rosary especially for May; the concept of the rosary as a "crown of roses" complements local traditions of wearing a flower wreath on the head. Latin hymns and litanies from the earliest Christian era name Mary as the "Mystical Rose" and by an array of rose epithets, or as a garden that bore Christ in the image of the rose. Ambrose declared that the blood of Christ in the Eucharist, transubstantiated from wine, was to be perceived as a rose. The five-petaled rose became a symbol of the Five Wounds of Christ and hence of the Resurrection of Jesus, Resurrection.
The living bodies and corpses of saints were said to exude a floral "odor of sanctity" as one of the most notable signs of their holiness. Pope Gregory I described the fragrance and luminosity of the rose as issuing from the blood of martyrs. Herman of Steinfeld exhaled a fragrance "like a garden full of roses, lilies, violets, poppies and all kinds of fragrant flowers" as he prayed. The bedridden virgin Lydwine of Schiedam was said to consume nothing but spiced wine, and wept "fragrant tears of blood" which she called her roses; when these dried on her cheeks overnight, they were gathered and kept in a box. The omen of her death was the opening of roses on a mystical rosebush, and when she was buried the bag of rose blood-tears was used as her pillow. Flowers, blood, and relics were interwoven in the imagery of Christian literature from the earliest period.
Miracle of the roses, Miracles involving roses are ascribed to some female saints, while roses are a distinguishing attribute of others ranging from Cecilia of Rome (d. 230 AD) to Thérèse of Lisieux (d. 1897). The floral iconography of Saint Cecilia includes a rose or floral wreath, a palm branch (symbol), palm branch, and a "tall sprig of almond leaves and flowers in her hand". Roses are among the most characteristic attributes of Mary, mother of Jesus, who became associated with the month of May, replacing goddesses such as Maia and Flora in the popular imagination. Mary is described in early Christian literature as a ''rosa pudoris'', "rose of modesty", and a rose among thorns. In the Middle Ages, roses, lilies and violets become the special flowers of Mary. In some Catholic cultures, offerings of flowers are still made to Mary, notably in Roman Catholicism in Mexico, Mexican devotional practices for Our Lady of Guadalupe. On the island of Pollap, in Micronesia, offerings of flowers before the cult statue of Mary are added to ceremonies of the rosary especially for May; the concept of the rosary as a "crown of roses" complements local traditions of wearing a flower wreath on the head. Latin hymns and litanies from the earliest Christian era name Mary as the "Mystical Rose" and by an array of rose epithets, or as a garden that bore Christ in the image of the rose. Ambrose declared that the blood of Christ in the Eucharist, transubstantiated from wine, was to be perceived as a rose. The five-petaled rose became a symbol of the Five Wounds of Christ and hence of the Resurrection of Jesus, Resurrection.
The living bodies and corpses of saints were said to exude a floral "odor of sanctity" as one of the most notable signs of their holiness. Pope Gregory I described the fragrance and luminosity of the rose as issuing from the blood of martyrs. Herman of Steinfeld exhaled a fragrance "like a garden full of roses, lilies, violets, poppies and all kinds of fragrant flowers" as he prayed. The bedridden virgin Lydwine of Schiedam was said to consume nothing but spiced wine, and wept "fragrant tears of blood" which she called her roses; when these dried on her cheeks overnight, they were gathered and kept in a box. The omen of her death was the opening of roses on a mystical rosebush, and when she was buried the bag of rose blood-tears was used as her pillow. Flowers, blood, and relics were interwoven in the imagery of Christian literature from the earliest period.
 Two days of the liturgical calendar have been called "Rose Sunday":
# The fourth Sunday of Lent is also known as ''Dominica de rosa'' ("Rose Sunday"), when Liturgical colours, rose-colored vestments may replace the purple or violet penance, penitential vestments of the season. On this day the Pope blesses the Golden Rose, a Jewellery, jewel in the shape of a rose. Benedict, a Canon (priest), canon of St. Peter's Basilica in the mid-12th century, recorded a ceremony on this day when the Pope carried a moss-wrapped rose in the Stations of the Cross. A 19th-century ecclesiastical lexicographer saw the Golden Rose as having functions analogous to the The Golden Bough (mythology), Golden Bough, with Mary assuming attributes of Persephone.
# In medieval Rome, a ''Dominica de Rosis'' (Sunday of Roses) or ''Pascha rosarum'' or ''rosatum'' was celebrated on the Sunday before Pentecost for the Octave (liturgical), octave of the Feast of the Ascension. The Pope delivered a sermon about the Holy Spirit on this day at the Santa Maria Rotunda, the basilica converted from the Pantheon, Rome, ancient Pantheon. Rose petals were showered through the Oculus (architecture), oculus in the dome to represent the descent of the tongues of flame. After dinner, a ''carnival, ludus Carnelevaris'' was celebrated with drinking among the knights and soldiers, followed by performances which featured the killing of animals that symbolized various sins.
:: Following this tradition, in medieval texts Pentecost is sometimes called ''Rosata Pascha'' or simply ''Rosalia''. Eventually, Pentecost itself took on the name of "Rose Sunday" as the two became conflated and customs were transferred from to the other. The custom of scattering roses for Pentecost spread and has continued to the modern era, as reflected in contemporary feast names such as the ', ', or '. Reflecting this custom, many churches are built with a "Holy Ghost hole" in the ceiling for the release of rose petals or white doves. The traditional Romanian language, Romanian name for Pentecost is ''Rusalii'' and is thought to derive from ''Rosalia''. The name ''Rusalii'' is also used in Russian language, Russian and Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, alongside the related term "Green week" (russian: Зелёные святки; uk, Зелені свята).
:: Some authors from the 19th and early-20th centuries speculated that this Rose Sunday was a Christianized form of the originally pagan festival.
Two days of the liturgical calendar have been called "Rose Sunday":
# The fourth Sunday of Lent is also known as ''Dominica de rosa'' ("Rose Sunday"), when Liturgical colours, rose-colored vestments may replace the purple or violet penance, penitential vestments of the season. On this day the Pope blesses the Golden Rose, a Jewellery, jewel in the shape of a rose. Benedict, a Canon (priest), canon of St. Peter's Basilica in the mid-12th century, recorded a ceremony on this day when the Pope carried a moss-wrapped rose in the Stations of the Cross. A 19th-century ecclesiastical lexicographer saw the Golden Rose as having functions analogous to the The Golden Bough (mythology), Golden Bough, with Mary assuming attributes of Persephone.
# In medieval Rome, a ''Dominica de Rosis'' (Sunday of Roses) or ''Pascha rosarum'' or ''rosatum'' was celebrated on the Sunday before Pentecost for the Octave (liturgical), octave of the Feast of the Ascension. The Pope delivered a sermon about the Holy Spirit on this day at the Santa Maria Rotunda, the basilica converted from the Pantheon, Rome, ancient Pantheon. Rose petals were showered through the Oculus (architecture), oculus in the dome to represent the descent of the tongues of flame. After dinner, a ''carnival, ludus Carnelevaris'' was celebrated with drinking among the knights and soldiers, followed by performances which featured the killing of animals that symbolized various sins.
:: Following this tradition, in medieval texts Pentecost is sometimes called ''Rosata Pascha'' or simply ''Rosalia''. Eventually, Pentecost itself took on the name of "Rose Sunday" as the two became conflated and customs were transferred from to the other. The custom of scattering roses for Pentecost spread and has continued to the modern era, as reflected in contemporary feast names such as the ', ', or '. Reflecting this custom, many churches are built with a "Holy Ghost hole" in the ceiling for the release of rose petals or white doves. The traditional Romanian language, Romanian name for Pentecost is ''Rusalii'' and is thought to derive from ''Rosalia''. The name ''Rusalii'' is also used in Russian language, Russian and Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, alongside the related term "Green week" (russian: Зелёные святки; uk, Зелені свята).
:: Some authors from the 19th and early-20th centuries speculated that this Rose Sunday was a Christianized form of the originally pagan festival.
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterr ...
, Rosalia or Rosaria was a festival of roses celebrated on various dates, primarily in May
May is the fifth month of the year in the Julian and Gregorian calendars and is the third of seven months to have a length of 31 days.
May is a month of spring in the Northern Hemisphere, and autumn in the Southern Hemisphere. Therefore, May ...
, but scattered through mid-July. The observance is sometimes called a ''rosatio'' ("rose-adornment") or the ''dies rosationis'', "day of rose-adornment," and could be celebrated also with violets
Violet identifies various plant taxa, particularly species in the genus ''Viola'', within which the common violet is the best known member in Eurasia and the common blue violet and common purple violet are the best known members in North America ...
''(violatio'', an adorning with violets, also ''dies violae'' or ''dies violationis'', "day of the "). As a commemoration of the dead, the ''rosatio'' developed from the custom of placing flowers at burial sites. It was among the extensive private religious practices by means of which the Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
cared for their dead, reflecting the value placed on tradition ''( mos maiorum'', "the way of the ancestors"), family lineage, and memorials ranging from simple inscriptions to grand public works. Several dates on the Roman calendar
The Roman calendar was the calendar used by the Roman Kingdom and Roman Republic. The term often includes the Julian calendar established by the reforms of the Roman dictator, dictator Julius Caesar and Roman emperor, emperor Augustus in the ...
were set aside as public holidays or memorial days devoted to the dead.
As a religious expression, a ''rosatio'' might also be offered to the cult statue of a deity or to other revered objects. In May, the Roman army
The Roman army (Latin: ) was the armed forces deployed by the Romans throughout the duration of Ancient Rome, from the Roman Kingdom (c. 500 BC) to the Roman Republic (500–31 BC) and the Roman Empire (31 BC–395 AD), and its medieval contin ...
celebrated the ''Rosaliae signorum'', rose festivals at which they adorned the military standards with garland
A garland is a decorative braid, knot or wreath of flowers, leaves, or other material. Garlands can be worn on the head or around the neck, hung on an inanimate object, or laid in a place of cultural or religious importance.
Etymology
From the ...
s. The rose festivals of private associations and clubs are documented by at least forty-one inscriptions in Latin and sixteen in Greek, where the observance is often called a ''rhodismos''.
Flowers were traditional symbols of rejuvenation, rebirth, and memory, with the red and purple of roses and violets felt to evoke the color of blood as a form of propitiation. Their blooming period framed the season of spring, with roses the last of the flowers to bloom and violets the earliest. As part of both festive and funerary banquets, roses adorned "a strange repast ... of life and death together, considered as two aspects of the same endless, unknown process." In some areas of the Empire, the Rosalia was assimilated to floral elements of spring festivals for Dionysus
In ancient Greek religion and myth, Dionysus (; grc, Διόνυσος ) is the god of the grape-harvest, winemaking, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstasy, festivity, and theatre. The Romans ...
, Adonis
In Greek mythology, Adonis, ; derived from the Canaanite word ''ʼadōn'', meaning "lord". R. S. P. Beekes, ''Etymological Dictionary of Greek'', Brill, 2009, p. 23. was the mortal lover of the goddess Aphrodite.
One day, Adonis was gored by ...
and others, but rose-adornment as a practice was not strictly tied to the cultivation of particular deities, and thus lent itself to Jewish and Christian commemoration. Early Christian writers transferred the imagery of garlands and crowns of roses and violets to the cult of the saints.
Cultural and religious background
 In Greece and Rome, wreaths and garlands of flowers and greenery were worn by both men and women for festive occasions. Garlands of roses and violets, combined or singly, adorn erotic scenes, bridal processions, and drinking parties in Greek lyric poetry from the Archaic period onward. In
In Greece and Rome, wreaths and garlands of flowers and greenery were worn by both men and women for festive occasions. Garlands of roses and violets, combined or singly, adorn erotic scenes, bridal processions, and drinking parties in Greek lyric poetry from the Archaic period onward. In Latin literature
Latin literature includes the essays, histories, poems, plays, and other writings written in the Latin language. The beginning of formal Latin literature dates to 240 BC, when the first stage play in Latin was performed in Rome. Latin literature ...
, to be "in the roses and violets" meant experiencing carefree pleasure. Floral wreaths and garlands "mark the wearers as celebrants and likely serve as an expression of the beauty and brevity of life itself." Roses and violets were the most popular flowers at Rome for wreaths, which were sometimes given as gifts.
Flowers were associated with or offered to some deities, particularly the goddesses Aphrodite
Aphrodite ( ; grc-gre, Ἀφροδίτη, Aphrodítē; , , ) is an ancient Greek goddess associated with love, lust, beauty, pleasure, passion, and procreation. She was syncretized with the Roman goddess . Aphrodite's major symbols inclu ...
(Roman Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never fa ...
), Persephone
In ancient Greek mythology and religion, Persephone ( ; gr, Περσεφόνη, Persephónē), also called Kore or Cora ( ; gr, Κόρη, Kórē, the maiden), is the daughter of Zeus and Demeter. She became the queen of the underworld after ...
(Proserpina
Proserpina ( , ) or Proserpine ( ) is an ancient Roman goddess whose iconography, functions and myths are virtually identical to those of Greek Persephone. Proserpina replaced or was combined with the ancient Roman fertility goddess Libera, whose ...
), and Chloris (Flora
Flora is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous) native plants. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora, as in the terms '' gut flora'' or '' skin flora''.
E ...
). Roses and fragrances are a special attribute of Aphrodite, and also of Dionysus
In ancient Greek religion and myth, Dionysus (; grc, Διόνυσος ) is the god of the grape-harvest, winemaking, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstasy, festivity, and theatre. The Romans ...
, particularly in Imperial-era poetry as a wine god for drinking parties or with the presence of Eros
In Greek mythology, Eros (, ; grc, Ἔρως, Érōs, Love, Desire) is the Greek god of love and sex. His Roman counterpart was Cupid ("desire").''Larousse Desk Reference Encyclopedia'', The Book People, Haydock, 1995, p. 215. In the ear ...
("Love, Desire"). The Greek romance novel ''Daphnis and Chloe
''Daphnis and Chloe'' ( el, Δάφνις καὶ Χλόη, ''Daphnis kai Chloē'') is an ancient Greek novel written in the Roman Empire, the only known work of the second-century AD Greek novelist and Hellenistic romance, romance writer Longus ...
'' (2nd century AD) describes a pleasure garden
A pleasure garden is a park or garden that is open to the public for recreation and entertainment. Pleasure gardens differ from other public gardens by serving as venues for entertainment, variously featuring such attractions as concert halls ...
, with roses and violets among its abundant flora, centered on a sacred space for Dionysus. At Rome Venus was a goddess of gardens as well as love and beauty. Venus received roses at her ritual cleansing ''(lavatio)'' on April 1
Events Pre-1600
* 33 – According to one historian's account, Jesus Christ's Last Supper is held.
* 527 – Byzantine Emperor Justin I names his nephew Justinian I as co-ruler and successor to the throne.
*1081 – Alexios I Ko ...
and at the wine festival (Vinalia
The Vinalia were Roman festivals of the wine harvest, wine vintage and gardens, held in honour of Jupiter and Venus. The ''Vinalia prima'' ("first Vinalia"), also known as the ''Vinalia urbana'' ("Urban Vinalia") was held on 23 April to bless an ...
) celebrated in her honor April 23.
A lavish display of flowers was an expression of conviviality and liberal generosity. An Imperial-era business letter
A business letter is a letter from one company to another, or such organizations and their customers, clients, or other external parties. The overall style of letter depends on the relationship between the parties concerned. Business letters can ...
surviving on papyrus
Papyrus ( ) is a material similar to thick paper that was used in ancient times as a writing surface. It was made from the pith of the papyrus plant, '' Cyperus papyrus'', a wetland sedge. ''Papyrus'' (plural: ''papyri'') can also refer to a ...
attempts to soothe a bridegroom
A bridegroom (often shortened to groom) is a man who is about to be married or who is newlywed.
When marrying, the bridegroom's future spouse (if female) is usually referred to as the bride. A bridegroom is typically attended by a best man ...
's mother upset that the rose harvest was insufficient to fill her order for the wedding; the suppliers compensated by sending 4,000 narcissus instead of the 2,000 she requested. While flowers were a part of Roman weddings, the bridegroom was more likely than the bride to wear a flower crown; Statius
Publius Papinius Statius ( Greek: Πόπλιος Παπίνιος Στάτιος; ; ) was a Greco-Roman poet of the 1st century CE. His surviving Latin poetry includes an epic in twelve books, the ''Thebaid''; a collection of occasional poetry, ...
(1st century AD) describes a groom as wearing a wreath of roses, violets, and lilies
''Lilium'' () is a genus of herbaceous flowering plants growing from bulbs, all with large prominent flowers. They are the true lilies. Lilies are a group of flowering plants which are important in culture and literature in much of the world. M ...
. When the emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereignty, sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), ...
made a formal arrival ''( adventus)'' at a city, garlands of flowers might be among the gestures of greeting from the welcome delegation. According to an account in the '' Historia Augusta'' ("presumably fictional"), the decadent emperor Heliogabalus buried the guests at one of his banquets in an avalanche of rose petals. In Greek culture, the ''phyllobolia'' was the showering of a victorious athlete or bridal couple with leaves or flower petals.

Classical mythology
Classical mythology, Greco-Roman mythology, or Greek and Roman mythology is both the body of and the study of myths from the ancient Greeks and ancient Romans as they are used or transformed by cultural reception. Along with philosophy and poli ...
preserves a number of stories in which blood and flowers are linked in divine metamorphosis.Miller, ''The Corporeal Imagination,'' p. 74. When Adonis
In Greek mythology, Adonis, ; derived from the Canaanite word ''ʼadōn'', meaning "lord". R. S. P. Beekes, ''Etymological Dictionary of Greek'', Brill, 2009, p. 23. was the mortal lover of the goddess Aphrodite.
One day, Adonis was gored by ...
, beloved of Aphrodite, was killed by a boar during a hunt, his blood produced a flower. A central myth of the Roman rites of Cybele
Cybele ( ; Phrygian: ''Matar Kubileya/Kubeleya'' "Kubileya/Kubeleya Mother", perhaps "Mountain Mother"; Lydian ''Kuvava''; el, Κυβέλη ''Kybele'', ''Kybebe'', ''Kybelis'') is an Anatolian mother goddess; she may have a possible forer ...
is the self-castration of her consort Attis
Attis (; grc-gre, Ἄττις, also , , ) was the consort of Cybele, in Phrygian and Greek mythology.
His priests were eunuchs, the ''Galli'', as explained by origin myths pertaining to Attis castrating himself. Attis was also a Phrygian v ...
, from whose blood a violet-colored flower sprang. In the Gnostic
Gnosticism (from grc, γνωστικός, gnōstikós, , 'having knowledge') is a collection of religious ideas and systems which coalesced in the late 1st century AD among Jewish and early Christian sects. These various groups emphasized pe ...
text ''On the Origin of the World
''On the Origin of the World'' is a Gnostic work dealing with creation and the end time. It was found among the texts in what is known as the Nag Hammadi library, in Codex II and Codex XIII, immediately following the '' Reality of the Rulers' ...
'', possibly dating to the early 4th century, the rose was the first flower to come into being, created from the virgin blood of Psyche
Psyche (''Psyché'' in French) is the Greek term for "soul" (ψυχή).
Psyche may also refer to:
Psychology
* Psyche (psychology), the totality of the human mind, conscious and unconscious
* ''Psyche'', an 1846 book about the unconscious by Car ...
("Soul") after she united sexually with Eros. In the 4th-century poem ''Cupid Crucified'' by the Gallo-Roman
Gallo-Roman culture was a consequence of the Romanization of Gauls under the rule of the Roman Empire. It was characterized by the Gaulish adoption or adaptation of Roman culture, language, morals and way of life in a uniquely Gaulish context ...
poet Ausonius
Decimius Magnus Ausonius (; – c. 395) was a Roman poet and teacher of rhetoric from Burdigala in Aquitaine, modern Bordeaux, France. For a time he was tutor to the future emperor Gratian, who afterwards bestowed the consulship on him ...
, the god Cupid (the Roman equivalent of Eros) is tortured in the underworld by goddesses disappointed in love, and the blood from his wounds causes roses to grow.Miller, ''The Corporeal Imagination,'' p. 75.
In Egyptian religion, funerary wreaths of laurel, palm
Palm most commonly refers to:
* Palm of the hand, the central region of the front of the hand
* Palm plants, of family Arecaceae
**List of Arecaceae genera
* Several other plants known as "palm"
Palm or Palms may also refer to:
Music
* Palm (ba ...
, feathers, papyrus
Papyrus ( ) is a material similar to thick paper that was used in ancient times as a writing surface. It was made from the pith of the papyrus plant, '' Cyperus papyrus'', a wetland sedge. ''Papyrus'' (plural: ''papyri'') can also refer to a ...
, or precious metals represented the " crown of justification" that the deceased was to receive when he was judged in the Weighing of the Heart
Ancient Egyptian afterlife beliefs were centered around a variety of complex rituals that were influenced by many aspects of Egyptian culture. Religion was a major contributor, since it was an important social practice that bound all Egyptians t ...
ceremony of the afterlife. In the Imperial period, the wreath might be roses, under the influence of the Romanized cult of Isis
Isis (; ''Ēse''; ; Meroitic: ''Wos'' 'a''or ''Wusa''; Phoenician: 𐤀𐤎, romanized: ʾs) was a major goddess in ancient Egyptian religion whose worship spread throughout the Greco-Roman world. Isis was first mentioned in the Old Kin ...
. The statue of Isis was adorned with roses following the ''Navigium Isidis
The ''Navigium Isidis'' or ''Isidis Navigium'' (trans. ''the vessel of Isis'') was an annual ancient Roman religious festival in honor of the goddess Isis, held on March 5. The festival outlived Christian persecution by Theodosius (391) and Ar ...
'', an Imperial holiday March 5 when a ceremonial procession represented the "sailing" of Isis. In the ''Metamorphoses
The ''Metamorphoses'' ( la, Metamorphōsēs, from grc, μεταμορφώσεις: "Transformations") is a Latin narrative poem from 8 CE by the Roman poet Ovid. It is considered his ''magnum opus''. The poem chronicles the history of the ...
'' of Apuleius
Apuleius (; also called Lucius Apuleius Madaurensis; c. 124 – after 170) was a Numidian Latin-language prose writer, Platonist philosopher and rhetorician. He lived in the Roman province of Numidia, in the Berber city of Madauros, modern- ...
, the protagonist Lucius is transformed into an ass, and after a journey of redemption returns to human form by eating roses and becoming an initiate into the mysteries of Isis
The mysteries of Isis were religious initiation rites performed in the cult of the Egyptian goddess Isis in the Greco-Roman world. They were modeled on other mystery rites, particularly the Eleusinian mysteries in honor of the Greek goddesses D ...
. A festival called the Rhodophoria, preserved in three Greek papyri, is the "rose-bearing" probably for Isis, or may be the Greek name for the Rosalia.
Roses and violets as funerary flowers
 Roses had funerary significance in Greece, but were particularly associated with death and entombment among the Romans. In Greece, roses appear on funerary
Roses had funerary significance in Greece, but were particularly associated with death and entombment among the Romans. In Greece, roses appear on funerary stele
A stele ( ),Anglicized plural steles ( ); Greek plural stelai ( ), from Greek , ''stēlē''. The Greek plural is written , ''stēlai'', but this is only rarely encountered in English. or occasionally stela (plural ''stelas'' or ''stelæ''), whe ...
s, and in epitaphs most often of girls. In Imperial-era Greek epitaphs, the death of an unmarried girl is compared to a budding rose cut down in spring; a young woman buried in her wedding clothes is "like a rose in a garden"; an eight-year-old boy is like the rose that is "the beautiful flower of the Erotes
In Ancient Greek religion and mythology, the Erotes () are a collective of winged gods associated with love and sexual intercourse. They are part of Aphrodite's retinue. ''Erotes'' (Greek ) is the plural of ''Eros'' ("Love, Desire"), who as a s ...
" ("Loves" or Cupids). As a symbol of both blooming youth and mourning, the rose often marks a death experienced as untimely or premature.Brenk, ''Clothed in Purple Light,'' p. 88. In the ''Iliad
The ''Iliad'' (; grc, Ἰλιάς, Iliás, ; "a poem about Ilium") is one of two major ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the '' Odys ...
'', Aphrodite anoints Hector
In Greek mythology, Hector (; grc, Ἕκτωρ, Hektōr, label=none, ) is a character in Homer's Iliad. He was a Trojan prince and the greatest warrior for Troy during the Trojan War. Hector led the Trojans and their allies in the defense o ...
's corpse with " ambrosial oil of roses" to maintain the integrity of his body against abuse in death. In Greek and Latin poetry, roses grow in the blessed afterlife of the Elysian Fields.
Bloodless sacrifice to the dead could include rose garlands and violets as well as libation
A libation is a ritual pouring of a liquid, or grains such as rice, as an offering to a deity or spirit, or in memory of the dead. It was common in many religions of antiquity and continues to be offered in cultures today.
Various substanc ...
s of wine, and Latin '' purpureus'' expressed the red-to-purple color range of roses and violets particularly as flowers of death. In ancient etymology, ''purpureus'' was thought related to Greek ''porphyreos'' in the sense of suffusing the skin with purple blood in bruising or wounding. The Augustan epic poet Vergil
Publius Vergilius Maro (; traditional dates 15 October 7021 September 19 BC), usually called Virgil or Vergil ( ) in English, was an ancient Roman poet of the Augustan period. He composed three of the most famous poems in Latin literature: t ...
uses the metaphor of a purple flower to describe the premature, bloody deaths of young men in battle: The death of Pallas
Pallas may refer to:
Astronomy
* 2 Pallas asteroid
** Pallas family, a group of asteroids that includes 2 Pallas
* Pallas (crater), a crater on Earth's moon
Mythology
* Pallas (Giant), a son of Uranus and Gaia, killed and flayed by Athena
* Pa ...
evokes both the violet of Attis and the hyacinth
Hyacinth or Hyacinthus may refer to:
Nature Plants
* Hyacinth (plant), genus ''Hyacinthus''
** '' Hyacinthus orientalis'', common hyacinth
* Grape hyacinth, '' Muscari'', a genus of perennial bulbous plants native to Eurasia
* Hyacinth bean, ''L ...
generated from the dying blood of Apollo
Apollo, grc, Ἀπόλλωνος, Apóllōnos, label=genitive , ; , grc-dor, Ἀπέλλων, Apéllōn, ; grc, Ἀπείλων, Apeílōn, label=Arcadocypriot Greek, ; grc-aeo, Ἄπλουν, Áploun, la, Apollō, la, Apollinis, label= ...
's beloved Hyacinthus. Claudian writes of the "bloody splendor" of roses in the meadow from which Proserpina will be abducted to the underworld, with hyacinths and violets contributing to the lush flora. Roses and the ominous presence of thorns may intimate bloodshed and mortality even in the discourse of love.
 Conversely, roses in a funerary context can allude to festive banqueting, since Roman families met at burial sites on several occasions throughout the year for libations and a shared meal that celebrated both the cherished memory of the beloved dead and the continuity of life through the family line. In Roman tomb painting, red roses often spill bountifully onto light ground. These ageless flowers created a perpetual Rosalia and are an expression of Roman beliefs in the soul's continued existence.
The bones or ashes of the deceased may be imagined as generating flowers, as in one Latin epitaph that reads:
Conversely, roses in a funerary context can allude to festive banqueting, since Roman families met at burial sites on several occasions throughout the year for libations and a shared meal that celebrated both the cherished memory of the beloved dead and the continuity of life through the family line. In Roman tomb painting, red roses often spill bountifully onto light ground. These ageless flowers created a perpetual Rosalia and are an expression of Roman beliefs in the soul's continued existence.
The bones or ashes of the deceased may be imagined as generating flowers, as in one Latin epitaph that reads:Here lies Optatus, a child ennobled by devotion: I pray that his ashes may be violets and roses, and I ask that the Earth, who is his mother now, be light upon him, for the boy's life was a burden to no one.Roses were planted at some tombs and
mausoleum
A mausoleum is an external free-standing building constructed as a monument enclosing the interment space or burial chamber of a deceased person or people. A mausoleum without the person's remains is called a cenotaph. A mausoleum may be consid ...
s, and adjacent grounds might be cultivated as gardens to grow roses for adornment or even produce
Produce is a generalized term for many farm-produced crops, including fruits and vegetables (grains, oats, etc. are also sometimes considered ''produce''). More specifically, the term ''produce'' often implies that the products are fresh and g ...
to sell for cemetery upkeep or administrative costs. In the 19th to the 21st centuries, a profusion of cut and cultivated flowers was still a characteristic of Italian cemeteries to a degree that distinguished them from Anglo-American
Anglo-Americans are people who are English-speaking inhabitants of Anglo-America. It typically refers to the nations and ethnic groups in the Americas that speak English as a native language, making up the majority of people in the world who spe ...
practice. This difference is one of the Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
practices criticized by some Protestants, especially in the 19th century, as too "pagan" in origin.
Rose and violet festivals
Domitian
Domitian (; la, Domitianus; 24 October 51 – 18 September 96) was a Roman emperor who reigned from 81 to 96. The son of Vespasian and the younger brother of Titus, his two predecessors on the throne, he was the last member of the Fl ...
(81–96 AD), and places the observance on June 20. The inscription was made by a priestly association ''(collegium
A (plural ), or college, was any association in ancient Rome that acted as a legal entity. Following the passage of the ''Lex Julia'' during the reign of Julius Caesar as Consul and Dictator of the Roman Republic (49–44 BC), and their rea ...
)'' in Lucania
Lucania was a historical region of Southern Italy. It was the land of the Lucani, an Oscan people. It extended from the Tyrrhenian Sea to the Gulf of Taranto.
It bordered with Samnium and Campania in the north, Apulia in the east, and Bruttiu ...
devoted to the woodland god Silvanus. It records vows for the wellbeing of the emperor and prescribes a sacrifice to Silvanus on five occasions in the year, among them the Rosalia. Although Silvanus is typically regarded as a deity of the woods and the wild, Vergil describes him as bearing flowering fennel and lilies. In other inscriptions, three donors to Silvanus had adopted the cultic name ''Anthus'' (Greek ''anthos'', "flower") and a fourth, of less certain reading, may have the Latin name ''Florus'', the masculine form of Flora
Flora is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous) native plants. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora, as in the terms '' gut flora'' or '' skin flora''.
E ...
. Since trees are the form of plant life most often emblematic of Silvanus, his connection with flowers is obscure. His female counterparts the Silvanae, primarily found in the Danubian provinces
The Danubian provinces of the Roman Empire were the provinces of the Lower Danube, within a geographical area encompassing the middle and lower Danube basins, the Eastern Alps, the Dinarides, and the Balkans. They include Noricum, Dacia ( Trajan ...
, are sometimes depicted carrying flower pots or wreaths. Through his epithet ''Dendrophorus'', "Tree-bearer," he was linked to the Romanized cult of Attis and Cybele in which celebrants called ''dendrophori'' participated.
When well-to-do people wrote a will and made end-of-life preparations, they might set aside funds for the maintenance of their memory and care ''(cura)'' after death, including rose-adornment. One epitaph records a man's provision for four annual observances in his honor: on the Parentalia
In ancient Rome, the Parentalia () or ''dies parentales'' (, "ancestral days") was a nine-day festival held in honor of family ancestors, beginning on 13 February.
Although the Parentalia was a holiday on the Roman religious calendar, its observa ...
, an official festival for honoring the dead February 13; his birthday ('' dies natalis''); and a ''Rosaria'' and ''Violaria''. Guilds and associations ''(collegia)'' often provided funeral benefits for members, and some were formed specifically for that purpose. Benefactors might fund communal meals and rose-days at which members of the college honored the dead. The College of Aesculapius and Hygia at Rome celebrated a Violet Day on March 22 and a Rose Day May 11, and these flower festivals are frequent among the occasions observed by dining clubs and burial societies.
Most evidence for the Rosalia comes from Cisalpine Gaul (northern Italy
Northern Italy ( it, Italia settentrionale, it, Nord Italia, label=none, it, Alta Italia, label=none or just it, Nord, label=none) is a geographical and cultural region in the northern part of Italy. It consists of eight administrative regions ...
), where twenty-four Latin inscriptions referring to it have been found. Ten Latin inscriptions come from the Italian peninsula, three from Macedonia, and four from Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to ...
, Illyria, and Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, coterminous westward with Noricum and upper Italy, and southward with Dalmatia and upper Moesia. Pannonia was located in the territory that is now wes ...
. Six Greek inscriptions come from Bithynia
Bithynia (; Koine Greek: , ''Bithynía'') was an ancient region, kingdom and Roman province in the northwest of Asia Minor (present-day Turkey), adjoining the Sea of Marmara, the Bosporus, and the Black Sea. It bordered Mysia to the southwest, Pa ...
, three from Macedonia, and one each from Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedon ...
, Scythia
Scythia (Scythian: ; Old Persian: ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) or Scythica (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ), also known as Pontic Scythia, was a kingdom created by the Scythians during the 6th to 3rd centuries BC in the Pontic–Caspian steppe.
Hi ...
, Mysia
Mysia (UK , US or ; el, Μυσία; lat, Mysia; tr, Misya) was a region in the northwest of ancient Asia Minor (Anatolia, Asian part of modern Turkey). It was located on the south coast of the Sea of Marmara. It was bounded by Bithynia on th ...
, Phrygia, Lydia, Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
and Arcadia
Arcadia may refer to:
Places Australia
* Arcadia, New South Wales, a suburb of Sydney
* Arcadia, Queensland
* Arcadia, Victoria
Greece
* Arcadia (region), a region in the central Peloponnese
* Arcadia (regional unit), a modern administrative un ...
.
 At
At Pergamon
Pergamon or Pergamum ( or ; grc-gre, Πέργαμον), also referred to by its modern Greek form Pergamos (), was a rich and powerful ancient Greek city in Mysia. It is located from the modern coastline of the Aegean Sea on a promontory on th ...
, Rosalia seems to have been a three-day festival May 24–26, beginning with an "Augustan day" ('' dies Augusti'', a day of Imperial cult
An imperial cult is a form of state religion in which an emperor or a dynasty of emperors (or rulers of another title) are worshipped as demigods or deities. "Cult" here is used to mean "worship", not in the modern pejorative sense. The cult may ...
marking a birthday, marriage, or other anniversary of the emperor or his family). The three-day Rosalia was among the occasions observed by a group of hymnodes, a male choir organized for celebrating Imperial cult, as recorded in a Greek inscription on an early 2nd-century altar. The ''eukosmos'', the officer of "good order" who presided over the group for a year, was to provide one '' mina'' (a monetary unit) and one loaf for celebrating the Rosalia on the Augustan day, which was the first day of the month called Panemos on the local calendar. On the second of Panemos, the group's priest provided wine, a table setting, one ''mina'', and three loaves for the Rosalia. The ''grammateus'', a secretary or administrator, was responsible for a ''mina'', a table setting worth one denarius
The denarius (, dēnāriī ) was the standard Roman silver coin from its introduction in the Second Punic War to the reign of Gordian III (AD 238–244), when it was gradually replaced by the antoninianus. It continued to be minted in very ...
, and one loaf for the third day of Rosalia. The group seems to have functioned like a ''collegium'' at Rome, and as a burial society for members.
Inscriptions from Acmonia
Acmonia or Akmonia ( grc, Ἀκμονία) is an ancient city of Phrygia Pacatiana, in Asia Minor, now known as Ahat Köyü. It is mentioned by Cicero (Pro Flacco, 15) and was a point on the road between Dorylaeum and Philadelphia. Under the R ...
, in Phrygia, show the Rosalia in the context of the religious pluralism
Religious pluralism is an attitude or policy regarding the diversity of religious belief systems co-existing in society. It can indicate one or more of the following:
* Recognizing and tolerating the religious diversity of a society or coun ...
of the Roman Empire. In 95 AD, a bequest was made for a burial society to ensure the annual commemoration of an individual named Titus Praxias. In addition to a graveside communal meal and cash gifts to members, 12 denarii were to be allocated for adorning the tomb with roses. The obligations of membership were both legally and religiously binding: the society had its own tutelary deities
A tutelary () (also tutelar) is a deity or a spirit who is a guardian, patron, or protector of a particular place, geographic feature, person, lineage, nation, culture, or occupation. The etymology of "tutelary" expresses the concept of safety an ...
who were invoked to oversee and ensure the carrying out of the deceased's wishes. These were ''Theos Sebastos'' (= '' Divus Augustus'' in Latin), Zeus
Zeus or , , ; grc, Δῐός, ''Diós'', label=Genitive case, genitive Aeolic Greek, Boeotian Aeolic and Doric Greek#Laconian, Laconian grc-dor, Δεύς, Deús ; grc, Δέος, ''Déos'', label=Genitive case, genitive el, Δίας, ''D� ...
under the local and unique epithet ''Stodmenos'', Asclepius
Asclepius (; grc-gre, Ἀσκληπιός ''Asklēpiós'' ; la, Aesculapius) is a hero and god of medicine in ancient Greek religion and mythology. He is the son of Apollo and Coronis, or Arsinoe, or of Apollo alone. Asclepius represe ...
the Savior
Savior or Saviour may refer to:
*A person who helps people achieve salvation, or saves them from something
Religion
* Mahdi, the prophesied redeemer of Islam who will rule for seven, nine or nineteen years
* Maitreya
* Messiah, a saviour or l ...
(Roman Aesculapius, as in the ''collegium'' above), and Artemis of Ephesus
The Temple of Artemis or Artemision ( gr, Ἀρτεμίσιον; tr, Artemis Tapınağı), also known as the Temple of Diana, was a Greek temple dedicated to an ancient, local form of the goddess Artemis (identified with Diana, a Roman god ...
. Acmonia also had a significant Greek-speaking Jewish community, and an inscription dating from the period 215–295 records similar arrangements made for a Jewish woman by her husband. It provides for an annual rose-adornment of the tomb by a legally constituted neighborhood or community association, with the solemn injunction "and if they do not deck it with roses each year, they will have to reckon with the justice of God." The formula "he will have to reckon with God" was used only among Jews and Christians in Phrygia, and there is a slighter possibility that the inscription might be Christian. The inscription is among the evidence that Judaism was not isolated from the general religious environment of the Imperial world, since a ''rosatio'' could be made without accompanying sacrifices at the tomb. Instead of multiple deities, the Jewish husband honoring his wife invoked the divine justice of his own God
In monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator, and principal object of faith. Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Oxford Companion to Philosophy'', Oxford University Press, 1995. God is typically ...
, and chose to participate in the customs of the community while adapting them in ways "acceptable to his Jewish faith".
 In Imperial-era Macedonia, several inscriptions mention the Rosalia as a commemorative festival funded by bequests to groups such as a ''vicianus'', a village or neighborhood association (from ''
In Imperial-era Macedonia, several inscriptions mention the Rosalia as a commemorative festival funded by bequests to groups such as a ''vicianus'', a village or neighborhood association (from ''vicus
In Ancient Rome, the Latin term (plural ) designated a village within a rural area () or the neighbourhood of a larger settlement. During the Republican era, the four of the city of Rome were subdivided into . In the 1st century BC, Augustus ...
''); ''thiasos
In Greek mythology and religion, the ''thiasus'' ( el, θίασος, thíasos), was the ecstatic retinue of Dionysus, often pictured as inebriated revelers. Many of the myths of Dionysus are connected with his arrival in the form of a processio ...
'', a legally constituted association, often having a religious character; or '' symposium'', in this sense a drinking and social club. In Thessalonica
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its metropolitan area, and the capital of the geographic region of ...
, a priestess of a ''thiasos'' bequeathed a tract of grapevines to pay for rose wreaths. If the Dionysian ''thiasos'' disbanded or failed in its duties, the property was to pass to a society of ''Dryophoroi'' ("Oak-Bearers"), or finally to the state.Kloppenborg and Ascough, ''Greco-Roman Associations,'' p. 373. In addition to associations of initiates into the mysteries of Dionysus, inscriptions in Macedonia and Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to ...
record bequests for rose-adornment to ''thiasoi'' of Diana (Artemis) and of the little-attested Thracian god or hero
A hero (feminine: heroine) is a real person or a main fictional character who, in the face of danger, combats adversity through feats of ingenuity, courage, or Physical strength, strength. Like other formerly gender-specific terms (like ...
Sourogethes, and to a gravedigger
A gravedigger is a cemetery worker who is responsible for digging a grave prior to a funeral service.
Description
If the grave is in a cemetery on the property of a church or other religious organization (part of, or called, a churchyard), ...
s' guild. The gravediggers were to kindle a tombside fire each year for the Rosalia, and other contexts suggest that the wreaths themselves might be burnt as offerings. A distinctive collocation that occurs a few times in Macedonian commemoration is an inscription prescribing the Rosalia accompanied by a relief
Relief is a sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces are bonded to a solid background of the same material. The term ''relief'' is from the Latin verb ''relevo'', to raise. To create a sculpture in relief is to give the impression that the ...
of the Thracian Horseman
The Thracian horseman (also "Thracian Rider" or "Thracian Heros") is a recurring motif depicted in reliefs of the Hellenistic and Roman periods in the Balkans—mainly Thrace, Macedonia, Thessaly and Moesia—roughly from the 3rd century BC to ...
.
Some scholars think that customs of the Rosalia were assimilated into Bacchic festivals of the dead by the Roman military, particularly in Macedonia and Thrace. A Greek inscription of 138 AD records a donation for rose-adornment ''(rhodismos)'' to the council in Histria, in modern Dobruja
Dobruja or Dobrudja (; bg, Добруджа, Dobrudzha or ''Dobrudža''; ro, Dobrogea, or ; tr, Dobruca) is a historical region in the Balkans that has been divided since the 19th century between the territories of Bulgaria and Romania. I ...
, an area settled by the Thracian Bessi, who were especially devoted to Dionysus. Macedonia was famed for its roses, but nearly all evidence for the Rosalia as such dates to the Roman period.
Bacchic rites
Although ivy and grapevines are the regular vegetative attributes ofDionysus
In ancient Greek religion and myth, Dionysus (; grc, Διόνυσος ) is the god of the grape-harvest, winemaking, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstasy, festivity, and theatre. The Romans ...
, at Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
roses and violets could be adornments for Dionysian feasts. In a fragment from a dithyramb
The dithyramb (; grc, διθύραμβος, ''dithyrambos'') was an ancient Greek hymn sung and danced in honor of Dionysus, the god of wine and fertility; the term was also used as an epithet of the god. Plato, in ''The Laws'', while discussing ...
praising Dionysus, the poet Pindar
Pindar (; grc-gre, Πίνδαρος , ; la, Pindarus; ) was an Ancient Greek lyric poet from Thebes. Of the canonical nine lyric poets of ancient Greece, his work is the best preserved. Quintilian wrote, "Of the nine lyric poets, Pindar ...
(5th century BC) sets a floral scene generated by the opening up of the Seasons ''(Horae
In Greek mythology the Horae () or Horai () or Hours ( grc-gre, Ὧραι, Hōrai, , "Seasons") were the goddesses of the seasons and the natural portions of time.
Etymology
The term ''horae'' comes from the Proto-Indo-European ("year").
F ...
)'', a time when Semele
Semele (; Ancient Greek: Σεμέλη ), in Greek mythology, was the youngest daughter of Cadmus and Harmonia (Greek goddess), Harmonia, and the mother of Dionysus by Zeus in one of his many origin myths.
Certain elements of the cult of Dionysu ...
, the mortal mother of Dionysus, is to be honored:

... as the chamber of the purple-robed Horai is opened,Dionysus was an equalizing figure of the democratic ''
the nectar-bearing flowers bring in the sweet-smelling spring.
Then, then, upon the immortal earth are cast
the lovely tresses of violets, and roses fitted to hair
and voices of songs echo to the accompaniment of pipes
and choruses come to Semele of the circling headband.
polis
''Polis'' (, ; grc-gre, πόλις, ), plural ''poleis'' (, , ), literally means "city" in Greek. In Ancient Greece, it originally referred to an administrative and religious city center, as distinct from the rest of the city. Later, it also ...
'' whose band of initiates ''(thiasos)'' provided a model for civic organizations. A form of Dionysia dating to pre- democratic Athens was the Anthesteria, a festival name some scholars derive from Greek ''anthos'', "flower, blossom", as did the Greeks themselves, connecting it to the blossoming grapevine. In the 6th century AD, the Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
antiquarian Joannes Lydus related the festival name to ''Anthousa'', which he said was the Greek equivalent of the Latin ''Flora''. The three-day festival, which took place at the threshold between winter and spring, involved themes of liminality
In anthropology, liminality () is the quality of ambiguity or disorientation that occurs in the middle stage of a rite of passage, when participants no longer hold their pre-ritual status but have not yet begun the transition to the status they w ...
and "opening up", but despite its importance in early Athens, many aspects elude certainty. It was primarily a celebration of opening the new wine from the previous fall's vintage. On the first day, "Dionysus" entered borne by a wheeled "ship" in a public procession, and was taken to the private chamber of the king's wife for a ritual union
''Ritual Union'' is the third studio album by Swedish electronic music band Little Dragon. It was released on 25 July 2011 by Peacefrog Records. The album reached number 47 in the band's native Sweden, as well as number 28 on the UK Albums Chart ...
with her; the precise ceremonies are unknown, but may be related to the myth of Ariadne
Ariadne (; grc-gre, Ἀριάδνη; la, Ariadne) was a Cretan princess in Greek mythology. She was mostly associated with mazes and labyrinths because of her involvement in the myths of the Minotaur and Theseus. She is best known for havi ...
, who became the consort of Dionysus after she was abandoned by the Athenian culture hero Theseus
Theseus (, ; grc-gre, Θησεύς ) was the mythical king and founder-hero of Athens. The myths surrounding Theseus his journeys, exploits, and friends have provided material for fiction throughout the ages.
Theseus is sometimes describ ...
.
 In keeping with its theme of new growth and transformation, the Anthesteria was also the occasion for a
In keeping with its theme of new growth and transformation, the Anthesteria was also the occasion for a rite of passage
A rite of passage is a ceremony or ritual of the passage which occurs when an individual leaves one group to enter another. It involves a significant change of status in society. In cultural anthropology the term is the Anglicisation of ''rite ...
from infancy to childhood—a celebratory moment given the high rate of infant mortality
Infant mortality is the death of young children under the age of 1. This death toll is measured by the infant mortality rate (IMR), which is the probability of deaths of children under one year of age per 1000 live births. The under-five morta ...
in the ancient world. Children between the age of three and four received a small jug ''(chous)'' specially decorated with scenes of children playing at adult activities. The ''chous'' itself is sometimes depicted on the vessel, adorned with a wreath. The following year, the child was given a ceremonial taste of wine from his ''chous''. These vessels are often found in children's graves, accompanying them to the underworld after a premature death.
The Anthesteria has also been compared with the Roman Lemuria
Lemuria (), or Limuria, was a continent proposed in 1864 by zoologist Philip Sclater, theorized to have sunk beneath the Indian Ocean, later appropriated by occultists in supposed accounts of human origins. The theory was discredited with the di ...
, with the second day a vulnerable time when the barrier between the world of the living and the dead became permeable, and the shades of the dead could wander the earth. On the third day, the ghosts were driven from the city, and Hermes Chthonios ("Underworld Hermes
Hermes (; grc-gre, wikt:Ἑρμῆς, Ἑρμῆς) is an Olympian deity in ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology. Hermes is considered the herald of the gods. He is also considered the protector of human heralds, travelle ...
") received sacrifices in the form of pots of grains and seeds. Although the identity of the shades is unclear, typically the restless dead are those who died prematurely.
Wine and roses
The priestess of Thessalonica who bequeathed a tract of vineyard for the maintenance of her memory required each Dionysian initiate who attended to wear a rose wreath. In a Dionysian context, wine, roses, and the color red are trappings of violence and funerals as well as amorous pursuits and revelry. Dionysus is described byPhilostratus
Philostratus or Lucius Flavius Philostratus (; grc-gre, Φιλόστρατος ; c. 170 – 247/250 AD), called "the Athenian", was a Greek sophist of the Roman imperial period. His father was a minor sophist of the same name. He was born probab ...
(d. ca. 250 AD) as wearing a wreath of roses and a red or purple cloak as he encounters Ariadne, whose sleep is a kind of death from which she is awakened and transformed by the god's love.
crown
A crown is a traditional form of head adornment, or hat, worn by monarchs as a symbol of their power and dignity. A crown is often, by extension, a symbol of the monarch's government or items endorsed by it. The word itself is used, partic ...
that symbolized Ariadne's immortal union with Dionysus underwent metamorphosis into a constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The origins of the e ...
, the Corona Borealis
Corona Borealis is a small constellation in the Northern Celestial Hemisphere. It is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Its brightest stars form a se ...
; in some sources, the ''corona'' was a diadem of jewels, but for the Roman dramatist Seneca
Seneca may refer to:
People and language
* Seneca (name), a list of people with either the given name or surname
* Seneca people, one of the six Iroquois tribes of North America
** Seneca language, the language of the Seneca people
Places Extrat ...
and others it was a garland of roses. In the ''Astronomica'' of Manilius
The gens Manilia was a plebeian family at ancient Rome. Members of this gens are frequently confused with the Manlii, Mallii, and Mamilii. Several of the Manilii were distinguished in the service of the Republic, with Manius Manilius obtaini ...
(1st century AD), Ariadne's crown is bejeweled with purple and red flowers—violets, hyacinths, poppies, and "the flower of the blooming rose, made red by blood"—and exerts a positive astrological influence on cultivating flower gardens, weaving garlands, and distilling perfume.
Dionysian scenes were common on Roman sarcophagi
In the burial practices of ancient Rome and Roman funerary art, marble and limestone sarcophagi elaborately carved in relief were characteristic of elite inhumation burials from the 2nd to the 4th centuries AD. At least 10,000 Roman sarcophagi ...
, and the persistence of love in the face of death may be embodied by attendant Cupids or Erotes. In Vergil's ''Aeneid
The ''Aeneid'' ( ; la, Aenē̆is or ) is a Latin Epic poetry, epic poem, written by Virgil between 29 and 19 BC, that tells the legendary story of Aeneas, a Troy, Trojan who fled the Trojan_War#Sack_of_Troy, fall of Troy and travelled to ...
'', purple flowers are strewn with the pouring of Bacchic
In ancient Greek religion and myth, Dionysus (; grc, Διόνυσος ) is the god of the grape-harvest, winemaking, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstasy, festivity, and theatre. The Roma ...
libation
A libation is a ritual pouring of a liquid, or grains such as rice, as an offering to a deity or spirit, or in memory of the dead. It was common in many religions of antiquity and continues to be offered in cultures today.
Various substanc ...
s during the funeral rites the hero Aeneas
In Greco-Roman mythology, Aeneas (, ; from ) was a Trojan hero, the son of the Trojan prince Anchises and the Greek goddess Aphrodite (equivalent to the Roman Venus). His father was a first cousin of King Priam of Troy (both being grandsons ...
conducts for his dead father. In the '' Dionysiaca'' of Nonnus
Nonnus of Panopolis ( grc-gre, Νόννος ὁ Πανοπολίτης, ''Nónnos ho Panopolítēs'', 5th century CE) was the most notable Greek epic poet of the Imperial Roman era. He was a native of Panopolis (Akhmim) in the Egyptian Theb ...
(late 4th–early 5th century AD), Dionysus mourns the death of the beautiful youth Ampelos
Ampelos ( grc-gre, Ἂμπελος, lit."Vine") or Ampelus (Latin) was a personification of the grapevine and lover of Dionysus in Greek and Roman mythology. He was a satyr that either turned into a Constellation or the grape vine, due to Dionys ...
by covering the body with flowers—roses, lilies, anemone
''Anemone'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the buttercup family Ranunculaceae. Plants of the genus are commonly called windflowers. They are native to the temperate and subtropical regions of all continents except Australia, New Zealand an ...
s—and infusing it with ambrosia. The dead boy's metamorphosis creates the first grapevine, which in turn produces the transformative substance of wine for human use.
Rites of Adonis
 The rites of Adonis ''( Adoneia)'' also came to be regarded as a Rosalia in the Imperial era. In one version of the myth, blood from Aphrodite's foot, pricked by a thorn, dyes the flowers produced from the body of Adonis when he is killed by the boar. In the ''Lament for Adonis'' attributed to Bion (2nd century BC), the tears of Aphrodite match the blood shed by Adonis drop by drop,
The rites of Adonis ''( Adoneia)'' also came to be regarded as a Rosalia in the Imperial era. In one version of the myth, blood from Aphrodite's foot, pricked by a thorn, dyes the flowers produced from the body of Adonis when he is killed by the boar. In the ''Lament for Adonis'' attributed to Bion (2nd century BC), the tears of Aphrodite match the blood shed by Adonis drop by drop,
and the blood and tears become flowers upon the ground. Of the blood comes the rose, and of the tears the windflower.According to myth, Adonis was born from the incestuous union of
Myrrha
Myrrha (Greek: , ''Mýrra''), also known as Smyrna (Greek: , ''Smýrna''), is the mother of Adonis in Greek mythology. She was transformed into a myrrh tree after having had intercourse with her father, and gave birth to Adonis in tree form. A ...
and her father. The delusional lust was a punishment from Aphrodite, whom Myrrha had slighted. The girl deceived her father with darkness and a disguise, but when he learned who she really was, his rage transformed her human identity and she became the fragrance-producing myrrh tree. The vegetative nature of Adonis is expressed in his birth from the tree. In one tradition, Aphrodite took the infant, hid him in a box ''(larnax
A larnax (plural: larnakes; grc, λάρναξ, ''lárnaks'', plural: , ''lárnakes'') is a type of small closed coffin, box or "ash-chest" often used in the Minoan civilization and in Ancient Greece as a container for human remains—either a co ...
'', a word often referring to chests for ash
Ash or ashes are the solid remnants of fires. Specifically, ''ash'' refers to all non-aqueous, non- gaseous residues that remain after something burns. In analytical chemistry, to analyse the mineral and metal content of chemical samples, ash ...
or other human remains), and gave him to the underworld goddess Persephone
In ancient Greek mythology and religion, Persephone ( ; gr, Περσεφόνη, Persephónē), also called Kore or Cora ( ; gr, Κόρη, Kórē, the maiden), is the daughter of Zeus and Demeter. She became the queen of the underworld after ...
to nurture. When he grew into a beautiful youth, both Aphrodite and Persephone—representing the realms of love and death—claimed him. Zeus decreed that Adonis would spend a third of the year with the heavenly Aphrodite, a third with chthonic Persephone, and a third on the mortal plane. The theme is similar to Persephone's own year divided between her underworld husband and the world above.
For J.G. Frazer, Adonis was an archetypal vegetative god, and H.J. Rose saw in the rites of Adonis "the outlines of an Oriental myth of the Great Mother and of her lover who dies as the vegetation dies, but comes back to life again." Robert A. Segal analyzed the death of Adonis as the failure of the " eternal child" ''( puer)'' to complete his rite of passage into the adult life of the city-state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world since the dawn of history, including cities such as ...
, and thus as a cautionary tale involving the social violations of "incest, murder, license, possessiveness, celibacy, and childlessness".
Women performed the ''Adoneia'' with ceremonial lamentation
A lament or lamentation is a passionate expression of grief, often in music, poetry, or song form. The grief is most often born of regret, or mourning. Laments can also be expressed in a verbal manner in which participants lament about somethin ...
and dirge
A dirge ( la, dirige, naenia) is a somber song or lament expressing mourning or grief, such as would be appropriate for performance at a funeral. Often taking the form of a brief hymn, dirges are typically shorter and less meditative than elegi ...
s, sometimes in the presence of an effigy of the dead youth that might be placed on a couch, perfumed, and adorned with greenery.Salapata, "Τριφίλητος Ἄδωνις," p. 35. As part of the festival, they planted " gardens of Adonis", container-grown annuals from "seeds planted in shallow soil, which sprang up quickly and withered quickly", compressing the cycle of life and death. The festival, often nocturnal, was not a part of the official state calendar of holidays, and as a private rite seems like the Rosalia to have had no fixed date. Although the celebration varied from place to place, it generally had two phases: joyful revelry like a marriage feast in celebration of the love between Aphrodite and Adonis, and ritual mourning for his death. Decorations and ritual trappings for the feast, including the dish gardens, were transformed for the funeral or destroyed as offerings: the garlanded couch became the lying-in bier
A bier is a stand on which a corpse, coffin, or casket containing a corpse is placed to lie in state or to be carried to the grave.''The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language'' (American Heritage Publishing Co., Inc., New York, ...
''( prothesis)''.
The iconography of Aphrodite and Adonis as a couple is often hard to distinguish in Greek art from that of Dionysus and Ariadne. In contrast to Greek depictions of the couple enjoying the luxury and delight of love, Roman paintings and sarcophagi almost always frame their love at the moment of loss, with the death of Adonis in Aphrodite's arms posing the question of resurrection
Resurrection or anastasis is the concept of coming back to life after death. In a number of religions, a dying-and-rising god is a deity which dies and is resurrected. Reincarnation is a similar process hypothesized by other religions, whic ...
. At Madaba
Madaba ( ar, مادبا; Biblical Hebrew: ''Mēḏəḇāʾ''; grc, Μήδαβα) is the capital city of Madaba Governorate in central Jordan, with a population of about 60,000. It is best known for its Byzantine and Umayyad mosaics, especi ...
, an Imperial city of the Province of Arabia
Arabia Petraea or Petrea, also known as Rome's Arabian Province ( la, Provincia Arabia; ar, العربية البترائية; grc, Ἐπαρχία Πετραίας Ἀραβίας) or simply Arabia, was a frontier province of the Roman Empi ...
in present-day Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Rive ...
, a series of mythological mosaics has a scene of Aphrodite and Adonis enthroned, attended by six Erotes and three Charites
In Greek mythology, the Charites ( ), singular ''Charis'', or Graces, were three or more goddesses of charm, beauty, nature, human creativity, goodwill, and fertility. Hesiod names three – Aglaea ("Shining"), Euphrosyne ("Joy"), and Tha ...
("Graces"). A basket of overturned roses near them has been seen as referring to the Rosalia.
In late antiquity
Late antiquity is the time of transition from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, generally spanning the 3rd–7th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin. The popularization of this periodization in English ha ...
, literary works set at a Rosalia—whether intended for performance at the actual occasion, or only using the occasion as a fictional setting—take the "lament for Adonis" as their theme. Shared language for the Roman festival of Rosalia and the floral aspects of the ''Adoneia'' may indicate similar or comparable practices, and not necessarily direct assimilation.
The violets of Attis
 From the reign of
From the reign of Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus (; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54) was the fourth Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Nero Claudius Drusus, Drusu ...
to that of Antoninus Pius
Antoninus Pius ( Latin: ''Titus Aelius Hadrianus Antoninus Pius''; 19 September 86 – 7 March 161) was Roman emperor from 138 to 161. He was the fourth of the Five Good Emperors from the Nerva–Antonine dynasty.
Born into a senatori ...
, a "holy week" in March developed for ceremonies of the Magna Mater ("Great Mother", also known as ''Mater Deum'', "Mother of the Gods," or Cybele
Cybele ( ; Phrygian: ''Matar Kubileya/Kubeleya'' "Kubileya/Kubeleya Mother", perhaps "Mountain Mother"; Lydian ''Kuvava''; el, Κυβέλη ''Kybele'', ''Kybebe'', ''Kybelis'') is an Anatolian mother goddess; she may have a possible forer ...
) and Attis. A preliminary festival on March 15 marked the discovery by shepherds or Cybele of the infant Attis among the reeds of a Phrygian river. The continuous ceremonies recommenced March 22 with the ''Arbor intrat'' ("The Tree enters") and lasted through March 27 or 28. For the day of ''Arbor intrat,'' the college of dendrophores ("tree-bearers") carried a pine tree to which was bound an effigy of Attis, wrapped in "woollen bandages like a corpse" and ornamented with violet wreaths. Lucretius
Titus Lucretius Carus ( , ; – ) was a Roman poet and philosopher. His only known work is the philosophical poem ''De rerum natura'', a didactic work about the tenets and philosophy of Epicureanism, and which usually is translated into En ...
(1st century BC) mentions roses and other unnamed flowers in the ecstatic procession of the Magna Mater for the Megalensia
The Megalesia, Megalensia, or Megalenses Ludi, was a festival celebrated in Ancient Rome from April 4 to April 10, in honour of Cybele, known to Romans as ''Magna Mater'' (Great Mother). The name of the festival derives from Greek ''Megale'' (μϵ� ...
in April.
The most vivid and complex account of how the violet was created out of violence in the Attis myth is given by the Christian apologist
Christian apologetics ( grc, ἀπολογία, "verbal defense, speech in defense") is a branch of Christian theology that defends Christianity.
Christian apologetics has taken many forms over the centuries, starting with Paul the Apostle in ...
Arnobius
Arnobius (died c. 330) was an early Christian apologist of Berber origin during the reign of Diocletian (284–305).
According to Jerome's ''Chronicle,'' Arnobius, before his conversion, was a distinguished Numidian rhetorician at Sicca Ven ...
(d. ca. 330), whose version best reflects cult practice in the Roman Imperial period. The story begins with a rock in Phrygia named ''Agdus'', from which had come the stones transformed to humans by Pyrrha
In Greek mythology, Pyrrha (; Ancient Greek: Πύρρα) was the daughter of Epimetheus and Pandora and wife of Deucalion of whom she had three sons, Hellen, Amphictyon, Orestheus; and three daughters Protogeneia, Pandora II and Thyia. Accordi ...
and Deucalion
In Greek mythology, Deucalion (; grc-gre, Δευκαλίων) was the son of Prometheus; ancient sources name his mother as Clymene, Hesione, or Pronoia.A scholium to ''Odyssey'' 10.2 (='' Catalogue'' fr. 4) reports that Hesiod called Deucal ...
to repopulate the world after the Flood
A flood is an overflow of water ( or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are an area of study of the discipline hydrol ...
. The Great Mother of the Gods customarily rested there, and there she was assailed by the lustful Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousandth t ...
. Unable to achieve his aim, the king of gods relieved himself by masturbating on the rock, from which was born Acdestis or Agdistis
Agdistis ( grc, Ἄγδιστις) is a deity of Greek, Roman, and Anatolian mythology who possesses both male and female sexual organs. They were closely associated with the Phrygian goddess Cybele.
Their androgyny was seen as a symbol ...
, a violent and supremely powerful hermaphroditic deity. After deliberations, the gods assign the ''cura'' of this audacity to Liber
In ancient Roman religion and mythology, Liber ( , ; "the free one"), also known as Liber Pater ("the free Father"), was a god of viticulture and wine, male fertility and freedom. He was a patron deity of Rome's plebeians and was part of the ...
, the Roman god identified with Dionysus: ''cura'' means variously "care, concern, cure, oversight."
Liber sets a snare, replacing the waters of Agdistis's favorite spring ''( fons)'' with pure wine. Necessity in time drives the thirsty Agdistis to drink, veins sucking up the torpor-inducing liquid. The trap is sprung: a noose, woven from hair, suspends Agdistis by the genitals, and the struggle to break free causes a self-castration. From the blood springs a pomegranate tree, its fruit so enticing that Nana
Nana, Nanna, Na Na or NANA may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Nana (given name), including a list of people and characters with the given name
* Nana (surname), including a list of people and characters with the surname
* Nana ( ...
, the daughter of the river god Sangarius
The Sakarya (Sakara River, tr, Sakarya Irmağı; gr, Σαγγάριος, translit=Sangarios; Latin: ''Sangarius'') is the third longest river in Turkey. It runs through the region known in ancient times as Phrygia. It was considered one of t ...
, ''in sinu reponit'', a euphemism in Imperial-era medical and Christian writing for "placed within the vagina". Nana becomes pregnant, enraging her father. He locks her away as damaged goods, and starves her. She is kept alive by fruits and other vegetarian food provided by the Mother of the Gods. When the infant is born, Sangarius orders that it be exposed
Expose, exposé, or exposed may refer to:
News sources
* Exposé (journalism), a form of investigative journalism
* '' The Exposé'', a British conspiracist website
Film and TV Film
* ''Exposé'' (film), a 1976 thriller film
* ''Exposed'' (1932 ...
, but it is discovered and reared by a goatherd. This child is Attis.
 The exceptionally beautiful Attis grows up favored by the Mother of the Gods and by Agdistis, who is his constant companion. Under the influence of wine, Attis reveals that his accomplishments as a hunter are owing to divine favor—an explanation for why wine is religiously prohibited ''(
The exceptionally beautiful Attis grows up favored by the Mother of the Gods and by Agdistis, who is his constant companion. Under the influence of wine, Attis reveals that his accomplishments as a hunter are owing to divine favor—an explanation for why wine is religiously prohibited ''(nefas
The vocabulary of ancient Roman religion was highly specialized. Its study affords important information about the religion, traditions and beliefs of the ancient Romans. This legacy is conspicuous in European cultural history in its influence on ...
)'' in his sanctuary and considered a pollution for those who would enter. Attis's relationship with Agdistis is characterized as '' infamis'', disreputable and socially marginalizing. The Phrygian king Midas
Midas (; grc-gre, Μίδας) was the name of a king in Phrygia with whom several myths became associated, as well as two later members of the Phrygian royal house.
The most famous King Midas is popularly remembered in Greek mythology for his ...
, wishing to redeem the boy ''(puer)'', arranges a marriage with his daughter, and locks down the city. The ''Mater Deum'', however, know Attis's fate ''(fatum)'': that he will be preserved from harm only if he avoids the bonds of marriage. Both the Mother of the Gods and Agdistis crash the party, and Agdistis spreads frenzy and madness among the convivial guests. In a detail that appears only in a vexed passage in the Christian source, the daughter of a concubine to a man named Gallus cuts off her breasts. Raging like a bacchant, Attis then throws himself under a pine tree, and cuts off his genitals as an offering to Agdistis. He bleeds to death, and from the flux of blood is born a violet flower.
The Mother of the Gods wraps the genitals "in the garment of the dead" and covers them with earth, an aspect of the myth attested in ritual by inscriptions regarding the sacrificial treatment of animal scrota. The would-be bride, whose name is Violet (Greek ''Ia)'', covers Attis's chest with woollen bands, and after mourning with Agdistis kills herself. Her dying blood is changed into purple violets. The tears of the Mother of the Gods become an almond tree, which signifies the bitterness of death. She then takes the pine tree to her sacred cave, and Agdistis joins her in mourning, begging Jupiter to restore Attis to life. This he cannot permit; but fate allows the body to never decay, the hair to keep growing, and the little finger
The little finger, or pinkie, also known as the baby finger, fifth digit, or pinky finger, is the most ulnar and smallest digit of the human hand, and next to the ring finger.
Etymology
The word "pinkie" is derived from the Dutch word ''p ...
to live and to wave in perpetual motion.
Arnobius explicitly states that the rituals performed in honor of Attis in his day reenact aspects of the myth as he has told it, much of which developed only in the Imperial period, in particular the conflict and intersections with Dionysian cult. For the ''Arbor intrat'' on March 22, the dendrophores carried the violet-wreathed tree of Attis to the Temple of the Magna Mater. As a ''dies violae'', the day of ''Arbor intrat'' recalled the scattering of violets onto graves for the Parentalia
In ancient Rome, the Parentalia () or ''dies parentales'' (, "ancestral days") was a nine-day festival held in honor of family ancestors, beginning on 13 February.
Although the Parentalia was a holiday on the Roman religious calendar, its observa ...
. The next day the dendrophores laid the tree to rest with noisy music that represented the Corybantes
According to Greek mythology, the Korybantes or Corybantes (also Corybants) (; grc-gre, Κορύβαντες) were the armed and crested dancers who worshipped the Phrygian goddess Cybele with drumming and dancing. They are also called the ''Ku ...
, youths who performed armed dances and in mythology served as guardians for infant gods. For the ''Dies Sanguinis'' ("Day of Blood") on March 24, the devotees lacerated themselves in a frenzy of mourning, spattering the effigy with the blood craved as "nourishment" by the dead. Some followers may have castrated themselves on this day, as a preliminary to becoming ''galli
A ''gallus'' (pl. ''galli'') was a eunuch priest of the Phrygian goddess Cybele (Magna Mater in Rome) and her consort Attis, whose worship was incorporated into the state religious practices of ancient Rome.
Origins
Cybele's cult may have ori ...
'', the eunuch
A eunuch ( ) is a male who has been castrated. Throughout history, castration often served a specific social function.
The earliest records for intentional castration to produce eunuchs are from the Sumerian city of Lagash in the 2nd millenni ...
priests of Cybele. Attis was placed in his "tomb" for the Sacred Night that followed.
According to Sallustius The names Sallustius/Saloustios and their vernacular variants Sallust(e) have been borne by many people:
* Sallust or Gaius Sallustius Crispus, historian of the 1st century BC
**Gardens of Sallust
* Gaius Sallustius Passienus Crispus, 1st-century A ...
, the cutting of the tree was accompanied by fasting
Fasting is the abstention from eating and sometimes drinking. From a purely physiological context, "fasting" may refer to the metabolic status of a person who has not eaten overnight (see " Breakfast"), or to the metabolic state achieved after ...
, "as though we were cutting off the further progress of generation; after this we are fed on milk as though being reborn; that is followed by rejoicings and garlands and as it were a new ascent to the gods." The garlands and rejoicing ''(Hilaria
The Hilaria (; Latin "the cheerful ones", a term derived from the borrowed adjective grc, ἱλαρός "cheerful, merry") were ancient Roman religious festivals celebrated on the March equinox to honor Cybele.
Origins
The term seems origi ...
)'' occurred on March 25, the vernal equinox on the Julian calendar
The Julian calendar, proposed by Roman consul Julius Caesar in 46 BC, was a reform of the Roman calendar. It took effect on , by edict. It was designed with the aid of Greek mathematicians and astronomers such as Sosigenes of Alexandr ...
, when Attis was in some sense "reborn" or renewed. Some early Christian sources associate this day with the resurrection of Jesus
The resurrection of Jesus ( grc-x-biblical, ἀνάστασις τοῦ Ἰησοῦ) is the Christian belief that God raised Jesus on the third day after his crucifixion, starting – or restoring – his exalted life as Christ and Lo ...
, and Damascius
Damascius (; grc-gre, Δαμάσκιος, 458 – after 538), known as "the last of the Athenian Neoplatonists," was the last scholarch of the neoplatonic Athenian school. He was one of the neoplatonic philosophers who left Athens after laws ...
saw it as a "liberation from Hades
Hades (; grc-gre, ᾍδης, Háidēs; ), in the ancient Greek religion and myth, is the god of the dead and the king of the underworld, with which his name became synonymous. Hades was the eldest son of Cronus and Rhea, although this also ...
". After a day of rest ''(Requietio),'' the ritual cleansing ''(Lavatio)'' of the Magna Mater was carried out on March 27. March 28 may have been a day of initiation into the mysteries of the Magna Mater and Attis at the Vaticanum.
Although scholars have become less inclined to view Attis within the rigid schema of "dying and rising vegetation god", the vegetal cycle remains integral to the funerary nature of his rites. The pine tree and pine cones were introduced to the iconography of Attis for their cult significance during the Roman period. A late 1st- or 2nd-century statue of Attis from Athens has him with a basket containing pomegranates, pine cones, and a nosegay of violets.
Vegetal aspects of spring festivals
Perceived connections with older spring festivals that involved roses helped spread and popularize the Rosalia, and the private ''dies violae'' or ''violaris'' of the Romans was enhanced by the public prominence of ''Arbor intrat'' ceremonies. The conceptual link between Attis and Adonis was developed primarily in the later Imperial period. TheNeoplatonic
Neoplatonism is a strand of Platonic philosophy that emerged in the 3rd century AD against the background of Hellenistic philosophy and religion. The term does not encapsulate a set of ideas as much as a chain of thinkers. But there are some id ...
philosopher Porphyry (d. ca. 305 AD) saw both Adonis and Attis as aspects of the "fruits of the earth":

Attis is the symbol of the blossoms which appear early in the spring, and fall off before the complete fertilization; whence they further attributed castration to him, from the fruits not having attained to seminal perfection: but Adonis was the symbol of the cutting of the perfect fruits.Porphyry linked Attis, Adonis, Korē (Persephone as "the Maiden", influencing "dry" or grain crops), and Dionysus (who influences soft and shell fruits) as deities of "seminal law":
For Korē was carried off byRoses and violets are typically among the flower species that populate the meadow from which Persephone was abducted asPluto Pluto (minor-planet designation: 134340 Pluto) is a dwarf planet in the Kuiper belt, a ring of bodies beyond the orbit of Neptune. It is the ninth-largest and tenth-most-massive known object to directly orbit the Sun. It is the largest ..., that is, the sun going down beneath the earth at seed-time; but Dionysus begins to sprout according to the conditions of the power which, while young, is hidden beneath the earth, yet produces fine fruits, and is an ally of the power in the blossom symbolized by Attis, and of the cutting of the ripened corn symbolized by Adonis.
Pluto
Pluto (minor-planet designation: 134340 Pluto) is a dwarf planet in the Kuiper belt, a ring of bodies beyond the orbit of Neptune. It is the ninth-largest and tenth-most-massive known object to directly orbit the Sun. It is the largest ...
's bride. The comparative mythologist Mircea Eliade
Mircea Eliade (; – April 22, 1986) was a Romanian historian of religion, fiction writer, philosopher, and professor at the University of Chicago. He was a leading interpreter of religious experience, who established paradigms in religiou ...
saw divine metamorphosis as a "flowing of life" between vegetal and human existence. When violent death interrupts the creative potential of life, it is expressed "in some other form: plant, fruit, flower". Eliade related the violets of Attis and the roses and anemones of Adonis to legends of flowers appearing on battlefields after the deaths of heroes.
Military ''Rosaliae''
TheRoman army
The Roman army (Latin: ) was the armed forces deployed by the Romans throughout the duration of Ancient Rome, from the Roman Kingdom (c. 500 BC) to the Roman Republic (500–31 BC) and the Roman Empire (31 BC–395 AD), and its medieval contin ...
celebrated the ''Rosaliae signorum,'' when the military standards ''(signa)'' were adorned with roses in a supplicatio
In ancient Roman religion, a ''supplicatio'' is a day of public prayer when the men, women, and children of Rome traveled in procession to religious sites around the city praying for divine aid in times of crisis. A ''supplicatio'' can also be a ...
n, on two dates in May. A.H. Hooey viewed the military rose festival as incorporating traditional spring festivals of vegetative deities. The festival is noted in the ''Feriale Duranum
The ''Feriale Duranum'' is a calendar of religious observances for a Roman military garrison at Dura-Europos on the Euphrates, Roman Syria, under the reign of Severus Alexander (224–235 AD).
History and description
The small papyrus roll w ...
'', a papyrus calendar for a cohort
Cohort or cohortes may refer to:
* Cohort (educational group), a group of students working together through the same academic curriculum
* Cohort (floating point), a set of different encodings of the same numerical value
* Cohort (military unit ...
stationed at Dura-Europos
Dura-Europos, ; la, Dūra Eurōpus, ( el, Δούρα Ευρωπός, Doúra Evropós, ) was a Hellenistic, Parthian, and Roman border city built on an escarpment above the southwestern bank of the Euphrates river. It is located near the vil ...
during the reign of Severus Alexander
Marcus Aurelius Severus Alexander (1 October 208 – 21/22 March 235) was a Roman emperor, who reigned from 222 until 235. He was the last emperor from the Severan dynasty. He succeeded his slain cousin Elagabalus in 222. Alexander himself was ...
(224–235 AD). The calendar is thought to represent a standard religious calendar issued to the military. The day of the earlier of the two ''Rosaliae'' is uncertain because of the fragmentary text, but coincided with the period of the Lemuria
Lemuria (), or Limuria, was a continent proposed in 1864 by zoologist Philip Sclater, theorized to have sunk beneath the Indian Ocean, later appropriated by occultists in supposed accounts of human origins. The theory was discredited with the di ...
, archaic festival days on May 9, 11, and 13 for propitiating shades ''(lemures
The lemures were shades or spirits of the restless or malignant dead in Roman religion, and are probably cognate with an extended sense of larvae (from Latin ''larva'', "mask") as disturbing or frightening. ''Lemures'' is the more common liter ...
'' or ''larvae)'' of those whose untimely death left them wandering the earth instead of passing into the underworld. The ceremonies of the Lemuria, in the vivid description of Ovid
Pūblius Ovidius Nāsō (; 20 March 43 BC – 17/18 AD), known in English as Ovid ( ), was a Roman poet who lived during the reign of Augustus. He was a contemporary of the older Virgil and Horace, with whom he is often ranked as one of the th ...
, featured the spitting of black beans as an especially potent apotropaic
Apotropaic magic (from Greek "to ward off") or protective magic is a type of magic intended to turn away harm or evil influences, as in deflecting misfortune or averting the evil eye. Apotropaic observances may also be practiced out of superst ...
gesture. The second of the ''Rosaliae signorum'' occurred on May 31
Events Pre-1600
* 455 – Emperor Petronius Maximus is stoned to death by an angry mob while fleeing Rome.
* 1223 – Mongol invasion of the Cumans: Battle of the Kalka River: Mongol armies of Genghis Khan led by Subutai defeat K ...
, the day before the Kalends of June. The feast day of June 1, devoted to the tenebrous '' Dea Carna'' ("Flesh Goddess" or "Food Goddess") and commonly called the "Bean Kalends
Cardea or Carda was the ancient Roman goddess of the hinge (Latin ''cardo, cardinis''), Roman doors being hung on pivot hinges. The Augustan poet Ovid conflates her with another archaic goddess named Carna, whose festival was celebrated on the ...
" ''(Kalendae Fabariae)'', may have pertained to rites of the dead and like the days of the Lemuria was marked on the calendar as ''nefastus
The vocabulary of ancient Roman religion was highly specialized. Its study affords important information about the religion, traditions and beliefs of the ancient Romans. This legacy is conspicuous in European cultural history in its influence o ...
'', a time when normal activities were religiously prohibited. In the later Empire, the ''Rosaliae signorum'' coincided with the third day of the "Bean Games" ''(Ludi
''Ludi'' (Latin plural) were public games held for the benefit and entertainment of the Roman people (''populus Romanus''). ''Ludi'' were held in conjunction with, or sometimes as the major feature of, Roman religious festivals, and were also ...
Fabarici)'' held May 29 – June 1, presumably in honor of Carna. A civilian inscription records a bequest for rose-adornment "on the Carnaria", interpreted by Mommsen as Carna's Kalends.
Sculpture from a 3rd-century military headquarters at Coria, in Roman Britain (Corbridge
Corbridge is a village in Northumberland, England, west of Newcastle upon Tyne, Newcastle and east of Hexham. Villages nearby include Halton, Northumberland, Halton, Acomb, Northumberland, Acomb, Aydon and Sandhoe.
Etymology
Corbridge was kno ...
, Northumberland
Northumberland () is a county in Northern England, one of two counties in England which border with Scotland. Notable landmarks in the county include Alnwick Castle, Bamburgh Castle, Hadrian's Wall and Hexham Abbey.
It is bordered by land on ...
), has been interpreted as representing the ''Rosaliae''. A 3rd-century inscription from Mogontiacum
Mainz () is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Mainz is on the left bank of the Rhine, opposite to the place that the Main joins the Rhine. Downstream of the confluence, the Rhine flows to the north-west, with Main ...
(present-day Mainz), in the province of Germania Superior, records the dedication of an altar to the Genius
Genius is a characteristic of original and exceptional insight in the performance of some art or endeavor that surpasses expectations, sets new standards for future works, establishes better methods of operation, or remains outside the capabili ...
of the military unit (a '' centuria''), on May 10. Although the inscription does not name the ''Rosaliae'', the date of the dedication, made in connection with Imperial cult, may have been chosen to coincide with it.
The ''Rosaliae signorum'' were part of devotional practices characteristic of the army surrounding the military standards. The Imperial historian Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
The surviving portions of his two major works—the ...
says that the army venerated the standards as if they were gods, and inscriptions record dedications ''(vota
VOTA (formerly known as Casting Pearls) is a Christian rock band from Lincoln, Nebraska, featuring Bryan Olesen, a former guitarist with Christian rock band Newsboys. Several of the band's songs have been featured on rotation with national radio ...
)'' made on their behalf. The day on which a legion
Legion may refer to:
Military
* Roman legion, the basic military unit of the ancient Roman army
* Spanish Legion, an elite military unit within the Spanish Army
* Legion of the United States, a reorganization of the United States Army from 179 ...
marked the anniversary of its formation was the ''natalis aquilae'', "the Eagle's birthday," in reference to the Roman eagle of the standard. All Roman military camps, including marching camp
In the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire, the Latin word ''castrum'', plural ''castra'', was a military-related term.
In Latin usage, the singular form ''castrum'' meant 'fort', while the plural form ''castra'' meant 'camp'. The singular and ...
s, were constructed around a central altar where daily sacrifices were made, surrounded by the standards planted firmly into the ground and by images of emperors and gods. Decorated units displayed gold and silver wreaths on their standards that represented the bestowal of living wreaths, and the Eagles and other ''signa'' were garlanded and anointed for lustrations, ceremonies for beginning a campaign, victories, crisis rituals, and Imperial holidays. Among these occasions was the wedding of the emperor Honorius in 398 AD, described in an epithalamium
An epithalamium (; Latin form of Greek ἐπιθαλάμιον ''epithalamion'' from ἐπί ''epi'' "upon," and θάλαμος ''thalamos'' nuptial chamber) is a poem written specifically for the bride on the way to her marital chamber. This form ...
by Claudian: the military standards are said to grow red with flowers, and the standard-bearers and soldiers ritually shower the imperial bridegroom with flowers ''purpureoque ... nimbo'', in a purple halo. In recounting a mutiny against Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus (; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54) was the fourth Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Nero Claudius Drusus, Drusu ...
in 42 AD, Suetonius avers that divine agency prevented the Eagles from being adorned or pulled from the earth to break camp by the legionaries
The Roman legionary (in Latin ''legionarius'', plural ''legionarii'') was a professional heavy infantryman of the Roman army after the Marian reforms. These soldiers would conquer and defend the territories of ancient Rome during the late Republi ...
who had violated their oath ''( sacramentum)''; reminded of their religious obligation, they were turned toward repentance ''(in paenitentiam religione conversis)''. Christian apologists
Christian apologetics ( grc, ἀπολογία, "verbal defense, speech in defense") is a branch of Christian theology that defends Christianity.
Christian apologetics has taken many forms over the centuries, starting with Paul the Apostle in ...
saw the veneration of the ''signa'' as central to the religious life of the Roman military, and Minucius Felix
__NOTOC__
Marcus Minucius Felix (died c. 250 AD in Rome) was one of the earliest of the Latin apologists for Christianity.
Nothing is known of his personal history, and even the date at which he wrote can be only approximately ascertained as betwe ...
tried to demonstrate that because of the cruciform
Cruciform is a term for physical manifestations resembling a common cross or Christian cross. The label can be extended to architectural shapes, biology, art, and design.
Cruciform architectural plan
Christian churches are commonly describe ...
shape, the soldiers had been worshipping the Christian cross without being aware of it.
Most evidence of the Rosalia from the Empire of the 1st–3rd centuries points toward festivals of the dead. Soldiers commemorated fallen comrades, and might swear an oath on the ''manes
In ancient Roman religion, the ''Manes'' (, , ) or ''Di Manes'' are chthonic deities sometimes thought to represent souls of deceased loved ones. They were associated with the ''Lares'', '' Lemures,'' '' Genii'', and ''Di Penates'' as deities ( ...
'' (deified spirits) of dead brothers-in-arms. Hooey, however, argued against interpreting the ''Rosaliae signorum'' as a kind of "poppy day". Roman rose festivals, in his view, were of two distinct and mutually exclusive kinds: the celebratory and licentious festivals of spring, and the somber cult of the dead. Transferred from the civilian realm, the old festivals of vegetative deities were celebrated in the Eastern Empire in a spirit of indulgence and luxury that was uniquely out of keeping with the public and Imperial character of other holidays on the ''Feriale Duranum''. This "carnival
Carnival is a Catholic Christian festive season that occurs before the liturgical season of Lent. The main events typically occur during February or early March, during the period historically known as Shrovetide (or Pre-Lent). Carnival typi ...
" view of the ''Rosaliae signorum'' was rejected by William Seston
William Seston (2 June 1900 – 2 October 1983) was a 20th-century French historian and epigrapher, a specialist of the history of the Roman Empire. He was professor at the Sorbonne and a member of the Académie des Inscriptions et Belles-Lettres ...
, who saw the May festivals as celebratory lustrations after the first battles of the military campaigning season, coordinate with the Tubilustrium
In Ancient Rome the month of March was the traditional start of the campaign season, and the Tubilustrium was a ceremony to make the army fit for war. The ceremony involved sacred trumpets called ''tubae''.
Johannes Quasten, however, argues ...
that fell on May 23 between the two rose-adornments.
The Tubilustrium was itself a purification ritual. Attested on calendars for both March 23 and May 23, it was perhaps originally monthly. The lustration ''(lustrum
A lūstrum (, plural lūstra) was a term for a five-year period in Ancient Rome.
It is distinct from the homograph ''lustrum'' ( ): a haunt of wild beasts (and figuratively, a den of vice), plural ''lustra'' ( ).Oxford Latin Desk Dictionary (20 ...
)'' was performed regarding the annunciatory trumpets (''tubi'' or '' tubae'', a long straight trumpet, and '' cornua'', which curved around the body) that were used to punctuate sacral games and ceremonies, funerals, and for signals and timekeeping in the military. The March 23 Tubilustrium coincided in the city of Rome with a procession of Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury (planet), Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Mars (mythology), Roman god of war. Mars is a terr ...
' armed priests the Salii
In ancient Roman religion, the Salii ( , ) were the "leaping priests" (from the verb ''saliō'' "leap, jump") of Mars supposed to have been introduced by King Numa Pompilius. They were twelve patrician youths, dressed as archaic warriors: an emb ...
, who clanged their sacred shields. In the later Empire, it had become assimilated into the "holy week" of Attis, occurring on the day when the tree rested at the Temple of the Magna Mater. As a pivotal point in the cycle of death/chaos and (re)birth/order, the day brought together noise rituals of wind and percussion instruments from different traditions, the clamor of the Corybantes
According to Greek mythology, the Korybantes or Corybantes (also Corybants) (; grc-gre, Κορύβαντες) were the armed and crested dancers who worshipped the Phrygian goddess Cybele with drumming and dancing. They are also called the ''Ku ...
or ''Kouretes'' who attended Cybele and Attis, and Roman ceremonies of apotropaic trumpet blasts or the beating of shields by the Salian priests, who were theologically identified with the ''Kouretes'' as early as the 1st century BC.
Tacitus records the performance of noise rituals on the trumpets by the military in conjunction with a lunar eclipse. The practice is found in other sources in a civilian context. Jörg Rüpke Jörg Rüpke (born 27 December 1962 in Herford, West Germany) is a German scholar of comparative religion and classical philology, recipient of the Gay-Lussac Humboldt Prize in 2008, and of the Advanced Grant of the European Research Council in 2011 ...
conjectures that the ''tubae'' were played monthly "to fortify the waning moon
Concerning the lunar month of ~29.53 days as viewed from Earth, the lunar phase or Moon phase is the shape of the Moon's directly sunlit portion, which can be expressed quantitatively using areas or angles, or described qualitatively using the t ...
(Luna
Luna commonly refers to:
* Earth's Moon, named "Luna" in Latin
* Luna (goddess), the ancient Roman personification of the Moon
Luna may also refer to:
Places Philippines
* Luna, Apayao
* Luna, Isabela
* Luna, La Union
* Luna, San Jose
Roma ...
)", one nundinal cycle
The nundinae (), sometimes anglicized to nundines,. were the market days of the ancient Roman calendar, forming a kind of weekend including, for a certain period, rest from work for the ruling class (patricians).
The nundinal cycle, market w ...
after the full moon
The full moon is the lunar phase when the Moon appears fully illuminated from Earth's perspective. This occurs when Earth is located between the Sun and the Moon (when the ecliptic longitudes of the Sun and Moon differ by 180°). This means ...
of the Ides Ides or IDES may refer to:
Calendar dates
* Ides (calendar), a day in the Roman calendar that fell roughly in the middle of the month. In March, May, July, and October it was the 15th day of the month; in other months it was the 13th.
**Ides of Mar ...
, since the Roman calendar was originally lunar
Lunar most commonly means "of or relating to the Moon".
Lunar may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Lunar'' (series), a series of video games
* "Lunar" (song), by David Guetta
* "Lunar", a song by Priestess from the 2009 album ''Prior t ...
. The ''signa'' and the trumpets were closely related in Roman military culture, both ceremonially and functionally, and on Trajan's Column
Trajan's Column ( it, Colonna Traiana, la, Columna Traiani) is a Roman triumphal column in Rome, Italy, that commemorates Roman emperor Trajan's victory in the Dacian Wars. It was probably constructed under the supervision of the architect Ap ...
the trumpets are shown pointing toward the standards during lustrations. Although Latin ''lustratio'' is usually translated as "purification", lustral ceremonies should perhaps be regarded as realignments and restorations of good order: "lustration is another word for maintaining, creating or restoring boundary lines between the centric order and the ex-centric disorder". The ''Rosaliae'' of the standards in May were contingent on ''supplicatio
In ancient Roman religion, a ''supplicatio'' is a day of public prayer when the men, women, and children of Rome traveled in procession to religious sites around the city praying for divine aid in times of crisis. A ''supplicatio'' can also be a ...
nes'', a broad category of propitiatory ritual that realigned the community, in this case the army, with the ''pax deorum
The vocabulary of ancient Roman religion was highly specialized. Its study affords important information about the religion, traditions and beliefs of the ancient Romans. This legacy is conspicuous in European cultural history in its influence on ...
'', the "treaty" or peace of the gods, by means of a procession, public prayers, and offerings. The military calendar represented by the ''Feriale Duranum'' prescribed ''supplicationes'' also for March 19–23, the period that began with the Quinquatria
In ancient Roman religion, the Quinquatria or Quinquatrus was a festival sacred to the Goddess Minerva, celebrated from the 19–23 of March. The older festivals were of Etruscan origin and were to celebrate the Spring equinox, the spring rebirt ...
, an ancient festival of Minerva
Minerva (; ett, Menrva) is the Roman goddess of wisdom, justice, law, victory, and the sponsor of arts, trade, and strategy. Minerva is not a patron of violence such as Mars, but of strategic war. From the second century BC onward, the Rom ...
and Mars, and concluded with a Tubilustrium. The Crisis of the Third Century
The Crisis of the Third Century, also known as the Military Anarchy or the Imperial Crisis (AD 235–284), was a period in which the Roman Empire nearly collapsed. The crisis ended due to the military victories of Aurelian and with the ascensio ...
prompted a revival and expansion of the archaic practice of ''supplicatio'' in connection with military and Imperial cult.
On the calendar
 In the later Empire, rose festivals became part of the iconography for the month of May. The date would vary locally to accommodate the blooming season. For month allegories in mosaics, May is often represented with floral wreaths, the fillets or ribbons worn for sacrifice, and wine
In the later Empire, rose festivals became part of the iconography for the month of May. The date would vary locally to accommodate the blooming season. For month allegories in mosaics, May is often represented with floral wreaths, the fillets or ribbons worn for sacrifice, and wine amphora
An amphora (; grc, ἀμφορεύς, ''amphoreús''; English plural: amphorae or amphoras) is a type of container with a pointed bottom and characteristic shape and size which fit tightly (and therefore safely) against each other in storag ...
e.Salzman, ''On Roman Time'' p. 97. May (Latin '' Maius'') began in the middle of the '' Ludi Florae'', a series of games in honor of the goddess Flora
Flora is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous) native plants. Sometimes bacteria and fungi are also referred to as flora, as in the terms '' gut flora'' or '' skin flora''.
E ...
that opened April 28 of the Julian calendar
The Julian calendar, proposed by Roman consul Julius Caesar in 46 BC, was a reform of the Roman calendar. It took effect on , by edict. It was designed with the aid of Greek mathematicians and astronomers such as Sosigenes of Alexandr ...
and concluded May 3. Flora was a goddess of flowers and blooming, and her festivities were enjoyed with a notable degree of sexual liberty. In the 2nd century AD, Philostratus connects rose garlands with Flora's festival. A Greek epigram from the ''Palatine Anthology
The ''Palatine Anthology'' (or ''Anthologia Palatina''), sometimes abbreviated ''AP'', is the collection of Greek poems and epigrams discovered in 1606 in the Palatine Library in Heidelberg. It is based on the lost collection of Constantinus Cep ...
'' has May personified announce "I am the mother of roses".
Among explanations for the month's name was that it derived from ''Maia
Maia (; Ancient Greek: Μαῖα; also spelled Maie, ; la, Maia), in ancient Greek religion and mythology, is one of the Pleiades and the mother of Hermes, one of the major Greek gods, by Zeus, the king of Olympus.
Family
Maia is the daugh ...
'', a goddess of growth or increase whose own name was sometimes said to come from the adjective ''maius'', "greater". Maia was honored in May with her son Mercury (Greek Hermes), a god of boundaries and commerce, and a conductor of souls to the afterlife. The theological identity of Maia was capacious; she was variously identified with goddesses such as ''Terra Mater
In ancient Roman religion and mythology, Tellus Mater or Terra Mater ("Mother Earth") is the personification of the Earth. Although Tellus and Terra are hardly distinguishable during the Imperial era, ''Tellus'' was the name of the original earth ...
'' ("Mother Earth"), the Good Goddess ''(Bona Dea
Bona Dea (; 'Good Goddess') was a goddess in ancient Roman religion. She was associated with chastity and fertility in Roman women, healing, and the protection of the state and people of Rome. According to Roman literary sources, she was brought ...
)'', the Great Mother Goddess ''(Magna Mater
Cybele ( ; Phrygian: ''Matar Kubileya/Kubeleya'' "Kubileya/Kubeleya Mother", perhaps "Mountain Mother"; Lydian ''Kuvava''; el, Κυβέλη ''Kybele'', ''Kybebe'', ''Kybelis'') is an Anatolian mother goddess; she may have a possible foreru ...
'', a title also for Cybele), Ops
In ancient Roman religion, Ops or ''Opis'' (Latin: "Plenty") was a fertility deity and earth goddess of Sabine origin. Her equivalent in Greek mythology was Rhea.
Iconography
In Ops' statues and coins, she is figured sitting down, as Chthon ...
("Abundance, Resources"), and Carna, the goddess of the Bean Kalends on June 1. Roses were distributed to the Arval Brothers
In ancient Roman religion, the Arval Brethren ( la, Fratres Arvales, "Brothers of the Fields") or Arval Brothers were a body of priests who offered annual sacrifices to the Lares and gods to guarantee good harvests. Inscriptions provide eviden ...
, an archaic priesthood of Rome, after their banquets for the May festival of Dea Dia
Dea Dia (Latin: "Goddess of Daylight", or "Bright Goddess") was a goddess of fertility and growth in ancient Roman religion. She was sometimes identified with Ceres, and sometimes with her Greek equivalent Demeter.
She was worshiped during ...
.
 Although the month opened with the revelry of Flora, in mid-May the Romans observed the three-day Lemuria for propitiating the wandering dead. The season of roses thus coincided with traditional Roman festivals pertaining to blooming and dying. The demand for flowers and perfumes for festal and funerary purposes made
Although the month opened with the revelry of Flora, in mid-May the Romans observed the three-day Lemuria for propitiating the wandering dead. The season of roses thus coincided with traditional Roman festivals pertaining to blooming and dying. The demand for flowers and perfumes for festal and funerary purposes made floriculture
Floriculture, or flower farming, is a branch of horticulture concerned with the cultivation of flowering and ornamental plants for gardens and for floristry, comprising the floral industry. The development of new varieties by plant breeding is ...
an important economic activity, especially for the rich estates of Roman Africa
Roman Africa may refer to the following areas of Northern Africa which were part of the Imperium Romanum and/or the Western/Byzantine successor empires :
; in the unified Roman empire :
* Africa (Roman province), with the great metropolis Carth ...
. One Roman tomb painting shows vendors displaying floral garlands for sale. Following the Lemuria, Mercury and Maia received a joint sacrifice during a merchants' festival on the Ides of May (the 15th). The Calendar of Filocalus
The ''Chronograph of 354'' (or "Chronography"), also known as the ''Calendar of 354'', is a compilation of chronological and calendrical texts produced in 354 AD for a wealthy Roman Christian named Valentinus by the calligrapher and illustrato ...
(354 AD) notes a flower fair on May 23, when the roses come to market ''( macellus)''. The month is illustrated for this calendar with a king of roses: a young man, wearing the long-sleeved robe called a ''dalmatica
The dalmatic is a long, wide-sleeved tunic, which serves as a liturgical vestment in the Catholic, Lutheran, Anglican, United Methodist, and some other churches. When used, it is the proper vestment of a deacon at Mass, Holy Communion or other se ...
'', carries a basket of roses on his left arm while holding a single flower in his right hand to smell. In other pictorial calendars, the Rose King or related imagery of the rose festival often substitutes for or replaces the traditional emblem of Mercury and his rites to represent May.
In Ovid's ''Fasti
In ancient Rome, the ''fasti'' (Latin plural) were chronological or calendar-based lists, or other diachronic records or plans of official and religiously sanctioned events. After Rome's decline, the word ''fasti'' continued to be used for simil ...
'', a poem about the Roman calendar, Flora as the divine representative of May speaks of her role in generating flowers from the blood of the dead: "through me glory springs from their wound". Ovid shows how her mythology weaves together themes of "violence, sexuality, pleasure, marriage, and agriculture." The Romans considered May an unpropitious month for weddings, a postponement that contributed to the popularity of June as a bridal month. Each day of the Lemuria in mid-May was a ''dies religiosus
The vocabulary of ancient Roman religion was highly specialized. Its study affords important information about the religion, traditions and beliefs of the ancient Romans. This legacy is conspicuous in European cultural history in its influence o ...
'', when it was religiously prohibited to begin any new undertaking, specifically including marriage "for the sake of begetting children".
In the 4th century, the Rosalia was marked on the official calendar as a public holiday at the amphitheater with games ''(ludi
''Ludi'' (Latin plural) were public games held for the benefit and entertainment of the Roman people (''populus Romanus''). ''Ludi'' were held in conjunction with, or sometimes as the major feature of, Roman religious festivals, and were also ...
)'' and theatrical performances. A calendar from Capua
Capua ( , ) is a city and ''comune'' in the province of Caserta, in the region of Campania, southern Italy, situated north of Naples, on the northeastern edge of the Campanian plain.
History
Ancient era
The name of Capua comes from the Etrus ...
dating to 387 AD notes a ''Rosaria'' at the amphitheater on May 13.
Christianization
 In the 6th century, a "Day of Roses" was held at Gaza, in the
In the 6th century, a "Day of Roses" was held at Gaza, in the Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
, as a spring festival that may have been a Christianized continuation of the Rosalia. John of Gaza wrote two anacreontic Anacreontics are verses in a metre used by the Greek poet Anacreon in his poems dealing with love and wine. His later Greek imitators (whose surviving poems are known as the ''Anacreontea'') took up the same themes and used the Anacreontic meter. ...
poems that he says he presented publicly on "the day of the roses", and declamation
Declamation (from the Latin: ''declamatio'') is an artistic form of public speaking. It is a dramatic oration designed to express through articulation, emphasis and gesture the full sense of the text being conveyed.
History
In Ancient Rome, decla ...
s by the Christian rhetorician Procopius
Procopius of Caesarea ( grc-gre, Προκόπιος ὁ Καισαρεύς ''Prokópios ho Kaisareús''; la, Procopius Caesariensis; – after 565) was a prominent late antique Greek scholar from Caesarea Maritima. Accompanying the Roman gen ...
and poetry by Choricius of Gaza Choricius of Gaza ( el, Χορίκιος) was a Gaza-based Greek sophist and rhetorician of Late Antiquity. With writings dating to the early sixth century, he flourished in the time of Anastasius I (AD 491–518) as a scholar and public orator. ...
are also set at rose-days.
Roses were in general part of the imagery of Early Christian funerary art, as was ivy. Martyrs
A martyr (, ''mártys'', "witness", or , ''marturia'', stem , ''martyr-'') is someone who suffers persecution and death for advocating, renouncing, or refusing to renounce or advocate, a religious belief or other cause as demanded by an external ...
were often depicted or described with flower imagery, or in ways that identified them with flowers. Paulinus of Nola
Paulinus of Nola (; la, Paulinus Nolanus; also Anglicized as Pauline of Nola; – 22 June 431) born Pontius Meropius Anicius Paulinus, was a Roman poet, writer, and senator who attained the ranks of suffect consul () and governor of Campan ...
(d. 431) reinterpreted traditions associated with the Rosalia in Christian terms for his natal poem ''(natalicium)'' about Saint Felix of Nola, set January 14:
Sprinkle the ground with flowers, adorn the doorways with garlands. Let winter breathe forth the purple beauty ''(purpureum)'' of spring; let the year be in flower before its time, and let nature submit to the holy day. For you also, earth, owe wreaths to the martyr’s tomb. But the holy glory of the doorway to the heavens encircles him, flowering with the twin wreaths of war and peace.At one of the earliest extant martyr shrines, now part of the
Basilica of Sant'Ambrogio
The Basilica of Sant'Ambrogio (official name: ''Basilica romana minore collegiata abbaziale prepositurale di Sant'Ambrogio'') is a church in the center of Milan, northern Italy.
History
One of the most ancient churches in Milan, it was built by ...
in Milan, a mosaic portrait dating perhaps as early as 397–402 depicts Saint Victor within a classically inspired wreath of lilies and roses, wheat stalks, grapes on the vine, and olive branches: the circular shape represents eternity, and the vegetation the four seasons. In the Christian imagination, the blood-death-flower pattern is often transferred from the young men of Classical myth—primarily Adonis and Attis—to female virgin martyrs. Eulalia of Mérida
Eulalia of Mérida (Augusta Emerita in 292 - Augusta Emerita 10 December, 304) was a young Roman Christian martyred in Augusta Emerita, the capital of Lusitania (modern Mérida, Spain), during the Persecution of Christians under Diocletian. O ...
is described by Prudentius
Aurelius Prudentius Clemens () was a Roman Christian poet, born in the Roman province of Tarraconensis (now Northern Spain) in 348.H. J. Rose, ''A Handbook of Classical Literature'' (1967) p. 508 He probably died in the Iberian Peninsula some ti ...
(d. ca. 413) as a "tender flower" whose death makes her "a flower in the Church's garland of martyrs": the flow of her purple blood produces purple violets and blood-red crocuses ''(purpureas violas sanguineosque crocos)'', which will adorn her relics. The rose can also symbolize the blood shed with the loss of virginity in the sacrament of marriage.
Drawing on the custom of floral crowns as awards in the Classical world, Cyprian
Cyprian (; la, Thaschus Caecilius Cyprianus; 210 – 14 September 258 AD''The Liturgy of the Hours according to the Roman Rite: Vol. IV.'' New York: Catholic Book Publishing Company, 1975. p. 1406.) was a bishop of Carthage and an early Christ ...
(d. 258) described heavenly crowns of flowers for the faithful in the afterlife: lilies for those who did good works, and an additional crown of roses for martyrs. In one early passion narrative, a martyr wears a rose crown ''(corona rosea)'' at a heavenly banquet. For Ambrose (d. 397), lilies were for virgins, violets for confessors of the faith, and roses for martyrs; of these, the imagery of the violet has no biblical precedent. In a passage influenced by Vergilian imagery, Ambrose enjoins young women who are virgins to "Let the rose of modesty and the lily of the spirit flourish in your gardens, and let banks of violets drink from the spring that is watered by the sacred blood." In the description of Jerome
Jerome (; la, Eusebius Sophronius Hieronymus; grc-gre, Εὐσέβιος Σωφρόνιος Ἱερώνυμος; – 30 September 420), also known as Jerome of Stridon, was a Christian priest, confessor, theologian, and historian; he is co ...
(d. 420), "a crown of roses and violets" is woven from the blood of Saint Paula
Paula of Rome (AD 347–404) was an ancient Roman saint and early Desert Mother. A member of one of the richest senatorial families which claimed descent from Agamemnon, Paula was the daughter of Blesilla and Rogatus, from the great clan of t ...
's martyrdom. Dante
Dante Alighieri (; – 14 September 1321), probably baptized Durante di Alighiero degli Alighieri and often referred to as Dante (, ), was an Italian poet, writer and philosopher. His ''Divine Comedy'', originally called (modern Italian: '' ...
later entwines Classical and Christian strands of imagery in his '' Paradiso'', linking the garland of saints with the rose ''corona'' of Ariadne, whom he imagines as translated to the heavens by it. The use of the term " rosary" (Latin ''rosarium
A rose garden or rosarium is a garden or park, often open to the public, used to present and grow various types of garden roses, and sometimes rose species. Most often it is a section of a larger garden. Designs vary tremendously and roses ma ...
'', a crown or garland of roses) for Marian
Marian may refer to:
People
* Mari people, a Finno-Ugric ethnic group in Russia
* Marian (given name), a list of people with the given name
* Marian (surname), a list of people so named
Places
* Marian, Iran (disambiguation)
* Marian, Queenslan ...
prayer beads
Prayer beads are a form of beadwork used to count the repetitions of prayers, chants, or mantras by members of various religions such as Hinduism, Buddhism, Shinto, Umbanda, Islam, Sikhism, the Baháʼí Faith, and some Christian denominati ...
was objected to by some Christians, including Alanus de Rupe
Alanus de Rupe (also Alan, Alain de la Roche, or Blessed Alain de la Roche); (c. 1428 – 8 September 1475) was a Roman Catholic theologian noted for his views on prayer. Some writers claim him as a native of Germany, others of Belgium; but his ...
, because it evoked the "profane" rose wreath of the Romans.
 Miracle of the roses, Miracles involving roses are ascribed to some female saints, while roses are a distinguishing attribute of others ranging from Cecilia of Rome (d. 230 AD) to Thérèse of Lisieux (d. 1897). The floral iconography of Saint Cecilia includes a rose or floral wreath, a palm branch (symbol), palm branch, and a "tall sprig of almond leaves and flowers in her hand". Roses are among the most characteristic attributes of Mary, mother of Jesus, who became associated with the month of May, replacing goddesses such as Maia and Flora in the popular imagination. Mary is described in early Christian literature as a ''rosa pudoris'', "rose of modesty", and a rose among thorns. In the Middle Ages, roses, lilies and violets become the special flowers of Mary. In some Catholic cultures, offerings of flowers are still made to Mary, notably in Roman Catholicism in Mexico, Mexican devotional practices for Our Lady of Guadalupe. On the island of Pollap, in Micronesia, offerings of flowers before the cult statue of Mary are added to ceremonies of the rosary especially for May; the concept of the rosary as a "crown of roses" complements local traditions of wearing a flower wreath on the head. Latin hymns and litanies from the earliest Christian era name Mary as the "Mystical Rose" and by an array of rose epithets, or as a garden that bore Christ in the image of the rose. Ambrose declared that the blood of Christ in the Eucharist, transubstantiated from wine, was to be perceived as a rose. The five-petaled rose became a symbol of the Five Wounds of Christ and hence of the Resurrection of Jesus, Resurrection.
The living bodies and corpses of saints were said to exude a floral "odor of sanctity" as one of the most notable signs of their holiness. Pope Gregory I described the fragrance and luminosity of the rose as issuing from the blood of martyrs. Herman of Steinfeld exhaled a fragrance "like a garden full of roses, lilies, violets, poppies and all kinds of fragrant flowers" as he prayed. The bedridden virgin Lydwine of Schiedam was said to consume nothing but spiced wine, and wept "fragrant tears of blood" which she called her roses; when these dried on her cheeks overnight, they were gathered and kept in a box. The omen of her death was the opening of roses on a mystical rosebush, and when she was buried the bag of rose blood-tears was used as her pillow. Flowers, blood, and relics were interwoven in the imagery of Christian literature from the earliest period.
Miracle of the roses, Miracles involving roses are ascribed to some female saints, while roses are a distinguishing attribute of others ranging from Cecilia of Rome (d. 230 AD) to Thérèse of Lisieux (d. 1897). The floral iconography of Saint Cecilia includes a rose or floral wreath, a palm branch (symbol), palm branch, and a "tall sprig of almond leaves and flowers in her hand". Roses are among the most characteristic attributes of Mary, mother of Jesus, who became associated with the month of May, replacing goddesses such as Maia and Flora in the popular imagination. Mary is described in early Christian literature as a ''rosa pudoris'', "rose of modesty", and a rose among thorns. In the Middle Ages, roses, lilies and violets become the special flowers of Mary. In some Catholic cultures, offerings of flowers are still made to Mary, notably in Roman Catholicism in Mexico, Mexican devotional practices for Our Lady of Guadalupe. On the island of Pollap, in Micronesia, offerings of flowers before the cult statue of Mary are added to ceremonies of the rosary especially for May; the concept of the rosary as a "crown of roses" complements local traditions of wearing a flower wreath on the head. Latin hymns and litanies from the earliest Christian era name Mary as the "Mystical Rose" and by an array of rose epithets, or as a garden that bore Christ in the image of the rose. Ambrose declared that the blood of Christ in the Eucharist, transubstantiated from wine, was to be perceived as a rose. The five-petaled rose became a symbol of the Five Wounds of Christ and hence of the Resurrection of Jesus, Resurrection.
The living bodies and corpses of saints were said to exude a floral "odor of sanctity" as one of the most notable signs of their holiness. Pope Gregory I described the fragrance and luminosity of the rose as issuing from the blood of martyrs. Herman of Steinfeld exhaled a fragrance "like a garden full of roses, lilies, violets, poppies and all kinds of fragrant flowers" as he prayed. The bedridden virgin Lydwine of Schiedam was said to consume nothing but spiced wine, and wept "fragrant tears of blood" which she called her roses; when these dried on her cheeks overnight, they were gathered and kept in a box. The omen of her death was the opening of roses on a mystical rosebush, and when she was buried the bag of rose blood-tears was used as her pillow. Flowers, blood, and relics were interwoven in the imagery of Christian literature from the earliest period.
Rose Sundays
 Two days of the liturgical calendar have been called "Rose Sunday":
# The fourth Sunday of Lent is also known as ''Dominica de rosa'' ("Rose Sunday"), when Liturgical colours, rose-colored vestments may replace the purple or violet penance, penitential vestments of the season. On this day the Pope blesses the Golden Rose, a Jewellery, jewel in the shape of a rose. Benedict, a Canon (priest), canon of St. Peter's Basilica in the mid-12th century, recorded a ceremony on this day when the Pope carried a moss-wrapped rose in the Stations of the Cross. A 19th-century ecclesiastical lexicographer saw the Golden Rose as having functions analogous to the The Golden Bough (mythology), Golden Bough, with Mary assuming attributes of Persephone.
# In medieval Rome, a ''Dominica de Rosis'' (Sunday of Roses) or ''Pascha rosarum'' or ''rosatum'' was celebrated on the Sunday before Pentecost for the Octave (liturgical), octave of the Feast of the Ascension. The Pope delivered a sermon about the Holy Spirit on this day at the Santa Maria Rotunda, the basilica converted from the Pantheon, Rome, ancient Pantheon. Rose petals were showered through the Oculus (architecture), oculus in the dome to represent the descent of the tongues of flame. After dinner, a ''carnival, ludus Carnelevaris'' was celebrated with drinking among the knights and soldiers, followed by performances which featured the killing of animals that symbolized various sins.
:: Following this tradition, in medieval texts Pentecost is sometimes called ''Rosata Pascha'' or simply ''Rosalia''. Eventually, Pentecost itself took on the name of "Rose Sunday" as the two became conflated and customs were transferred from to the other. The custom of scattering roses for Pentecost spread and has continued to the modern era, as reflected in contemporary feast names such as the ', ', or '. Reflecting this custom, many churches are built with a "Holy Ghost hole" in the ceiling for the release of rose petals or white doves. The traditional Romanian language, Romanian name for Pentecost is ''Rusalii'' and is thought to derive from ''Rosalia''. The name ''Rusalii'' is also used in Russian language, Russian and Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, alongside the related term "Green week" (russian: Зелёные святки; uk, Зелені свята).
:: Some authors from the 19th and early-20th centuries speculated that this Rose Sunday was a Christianized form of the originally pagan festival.
Two days of the liturgical calendar have been called "Rose Sunday":
# The fourth Sunday of Lent is also known as ''Dominica de rosa'' ("Rose Sunday"), when Liturgical colours, rose-colored vestments may replace the purple or violet penance, penitential vestments of the season. On this day the Pope blesses the Golden Rose, a Jewellery, jewel in the shape of a rose. Benedict, a Canon (priest), canon of St. Peter's Basilica in the mid-12th century, recorded a ceremony on this day when the Pope carried a moss-wrapped rose in the Stations of the Cross. A 19th-century ecclesiastical lexicographer saw the Golden Rose as having functions analogous to the The Golden Bough (mythology), Golden Bough, with Mary assuming attributes of Persephone.
# In medieval Rome, a ''Dominica de Rosis'' (Sunday of Roses) or ''Pascha rosarum'' or ''rosatum'' was celebrated on the Sunday before Pentecost for the Octave (liturgical), octave of the Feast of the Ascension. The Pope delivered a sermon about the Holy Spirit on this day at the Santa Maria Rotunda, the basilica converted from the Pantheon, Rome, ancient Pantheon. Rose petals were showered through the Oculus (architecture), oculus in the dome to represent the descent of the tongues of flame. After dinner, a ''carnival, ludus Carnelevaris'' was celebrated with drinking among the knights and soldiers, followed by performances which featured the killing of animals that symbolized various sins.
:: Following this tradition, in medieval texts Pentecost is sometimes called ''Rosata Pascha'' or simply ''Rosalia''. Eventually, Pentecost itself took on the name of "Rose Sunday" as the two became conflated and customs were transferred from to the other. The custom of scattering roses for Pentecost spread and has continued to the modern era, as reflected in contemporary feast names such as the ', ', or '. Reflecting this custom, many churches are built with a "Holy Ghost hole" in the ceiling for the release of rose petals or white doves. The traditional Romanian language, Romanian name for Pentecost is ''Rusalii'' and is thought to derive from ''Rosalia''. The name ''Rusalii'' is also used in Russian language, Russian and Ukrainian language, Ukrainian, alongside the related term "Green week" (russian: Зелёные святки; uk, Зелені свята).
:: Some authors from the 19th and early-20th centuries speculated that this Rose Sunday was a Christianized form of the originally pagan festival.
See also
* Ancient Greek funeral and burial practices * Roman funerals and burial * a festival in memory of the dead of the ancient SlavsReferences
{{Roman religion (festival) Ancient Roman festivals May observances June observances July observances Flower festivals in Europe Flower festivals in Italy